Ubuntu is a popular Linux distribution that has gained a significant following in the open-source community. Developed by Canonical Ltd., Ubuntu offers a powerful and user-friendly computing experience that is highly customizable to meet individual needs.
One of the key features that make Ubuntu stand out is its extensive use of keyboard shortcuts. These shortcuts allow users to accomplish tasks faster and more efficiently, making the Ubuntu experience even more seamless.
Mastering Ubuntu keyboard shortcuts
In this guide, we will explore the world of Ubuntu keyboard shortcuts, their benefits, and how to master them to streamline your workflow and enhance your productivity.
The Super Key (Windows Key)
Before diving into the world of Ubuntu keyboard shortcuts, it is important to understand the role of the Super key. Located between the Ctrl and Alt keys, the Super key is a crucial component in executing many of the most useful keyboard shortcuts in Ubuntu. It is also commonly referred to as the “Windows key” due to its similar functionality on Windows-based systems.
For users who are using Ubuntu with a macOS keyboard or running Ubuntu as a Virtual Machine on macOS, the Super key is equivalent to the “Command” (cmd) key. Understanding the role of the Super key is essential in mastering Ubuntu keyboard shortcuts and improving your overall productivity.
Note: In this post, we will be using the word “Super key” instead of the popular “Windows key.”
1. Terminal shortcuts
The Terminal is a powerful tool that allows users to interact with their Ubuntu system through a command-line interface. While it may seem daunting to those who are new to Linux, the terminal offers a level of control and flexibility that cannot be matched by graphical user interfaces alone. Feel free to check out our comprehensive post about The Ubuntu terminal: Getting started with the command line interface.
In order to fully utilize the capabilities of the terminal, it is important to learn some of the most useful keyboard shortcuts. These shortcuts allow users to perform common tasks quickly and efficiently, from navigating the file system to managing processes and more. By mastering terminal shortcuts, users can harness the full power of the Ubuntu command-line interface and streamline their workflow for increased productivity.
Terminal window and tabs shortcuts
Ctrl+Alt+T: This shortcut launches the Terminal application, making it quick and easy to access the command-line interface and start entering commands.
F11: This shortcut maximizes your Terminal window to full screen. You can also use it to leave the “full screen” mode.
Ctrl +Shift +Q: This shortcut closes the current terminal window, allowing users to quickly exit the Terminal application when they are finished using it.
Ctrl+Shift +T: This shortcut opens a new tab within the Terminal application, making it easy to multitask and run multiple commands simultaneously.
Ctrl+Shift+W: This shortcut closes the current tab within the Terminal application, allowing users to close out specific tabs when they are finished with them.
Ctrl+Page Up: This shortcut allows users to switch to the previous tab within the Terminal application, making it easy to navigate between open tabs and keep multiple commands organized.
Ctrl+Page Down: This shortcut allows users to switch to the next tab within the Terminal application, providing quick access to different open tabs and the commands running within them.
Ctrl+Shift+Page Up: This shortcut allows users to move to the tab to the left of the current tab within the Terminal application, making it easy to reorder open tabs and keep related commands together.
Ctrl+Shift +Page Down: This shortcut allows users to move to the tab to the right of the current tab within the Terminal application, providing a quick way to navigate between different open tabs and commands.
Alt+1 to Alt+9: These shortcuts allow users to quickly switch to a specific tab within the Terminal application. For example, pressing Alt+2 will switch to the second open tab, while Alt+9 will switch to the ninth open tab.
Alt+0: This shortcut allows users to quickly switch to the tenth open tab within the Terminal application, making it easy to keep multiple commands organized and easily accessible.
Command-line editing shortcuts
Shift+Ctrl+C: This shortcut allows users to copy the highlighted text. Simply highlight the text with the mouse or touchpad and press Shift+Ctrl+C to copy.
Shift+Ctrl+V: This shortcut allows users to paste copied text into a terminal window. If pasting into an application like an editor, use the conventional Ctrl+V shortcut.
Ctrl+A or Home: These shortcuts allow users to move to the start of a command line.
Ctrl+E or End: These shortcuts allow users to move to the end of a command line.
Alt+B or Ctrl+Left Arrow: These shortcuts allow users to move the cursor backward one word.
Ctrl+B or Left Arrow: These shortcuts allow users to move the cursor backward one character.
Alt+F or Ctrl+Right Arrow: These shortcuts allow users to move the cursor forward one word.
Ctrl+F or Right Arrow: To move the cursor forward one character, users can use either Ctrl+F or the Right Arrow key.
Ctrl+XX: This shortcut allows users to quickly hop between the current position of the cursor and the start of the line. Hold down Ctrl and press X twice, quickly.
Ctrl+D or Delete: This shortcut allows users to delete the character under the cursor.
Ctrl+U: This shortcut allows users to delete all characters before the cursor. Additionally, users can use Ctrl+E followed by Ctrl+U to delete the entire line.
Alt+D: This shortcut allows users to delete all characters after the cursor to the end of the line.
Ctrl+H or Backspace: This shortcut allows users to delete the character before the cursor.
Terminal output shortcuts
Ctrl+L: This shortcut allows users to clear the terminal window and remove all previous output. This is the same as typing clear in the command line.
Ctrl+S: This shortcut allows users to stop scrolling output and freeze the output from a program. However, the program will continue to run in the background.
Ctrl+Q: This shortcut allows users to restart scrolling output if it has been stopped with Ctrl+S. This will resume the output of the program that was frozen using Ctrl+S.
Shift+Ctrl++ (Ctrl + Shift, then press the + sign): This shortcut will “zoom in” then Terminal output making the text appear larger and much more visible.
Shift+Ctrl+- (Ctrl + Shift, then press the – sign): This shortcut will “zoom out” then Terminal output making the text appear smaller.
Ctrl+0 (that is, Ctrl and 0, “zero”): This shortcut will return the Terminal output to the normal size. That’s if you had zoomed in or zoomed out.
Shortcuts to search the terminal
Shift+Ctrl+F: This shortcut opens the “Find” dialog box, allowing users to search for a specific term or phrase in the command line output.
Shift+Ctrl+G: Once a search term has been found using the “Find” command, this shortcut allows users to find the next occurrence of the search term.
Shift+Ctrl+H: This shortcut allows users to find the previous occurrence of the search term found using the “Find” command.
Shift+Ctrl+J: This shortcut clears any text highlights, such as those that are created when using the “Find” command.
2. Desktop shortcuts
Desktop shortcuts are a convenient way to access frequently used applications or files on your Ubuntu system. These shortcuts are essentially links that allow you to quickly launch an application or open a file without having to navigate through multiple folders and menus.
Alt+F2: Opens a dialog box where you can quickly run commands or launch applications without navigating through menus.
Super+D: Minimizes all open windows and shows your desktop.
Super+Tab or Alt+Tab: Switches between open applications. Brings up a menu showing all currently open applications. You can use the arrow keys or mouse to select the application you want to switch to.
Ctrl+Alt+Up/Down Arrow: Moves to the previous or next workspace.
Shift+Ctrl+Alt+Up/Down Arrow: Moves an application from one workspace to another.
Super+Left/Right/Up/Down Arrow: Organizes your desktop. You can snap a window to the left or right side of the screen, maximize a window, or restore it to its previous size.
Super+M or Super+V: Displays the notifications area and calendar.
Super+Space: Switches between input sources for multiple keyboards or languages set up on your system.
Super + L: Locks your screen, making it necessary to enter your password to log back in.
Ctrl+Alt+Del: Logs you out of your current session, helpful when you need to switch users or restart your system.
3. Application keyboard shortcuts
Certainly! Application shortcuts are keyboard combinations that allow you to perform various tasks within an application without having to navigate through menus or click on icons. These shortcuts can help you work more efficiently and quickly, and are often customizable so that you can set them up to fit your specific needs.
Ctrl+Q or Ctrl+W or Alt+F4: These shortcuts are used to close an application. Pressing any of these keys will close the current window or tab in the application you are using.
Ctrl+P: This shortcut is used to open the Print dialog. You can use this dialog to select a printer, set print options, and print the current document or image.
Ctrl+S: This shortcut is used to save the current file. If you have made changes to a file and want to save them, pressing Ctrl+S will save the changes to the file.
Shift+Ctrl+S: This shortcut is used to open the File Save dialog. You can use this dialog to save a file with a new name or in a different location.
Ctrl+O: This shortcut is used to open the Open File dialog. You can use this dialog to browse for and open a file in the application you are using.
How to create custom keyboard shortcuts on Ubuntu
Below is a step-by-step guide on how to create custom keyboard shortcuts on Ubuntu:
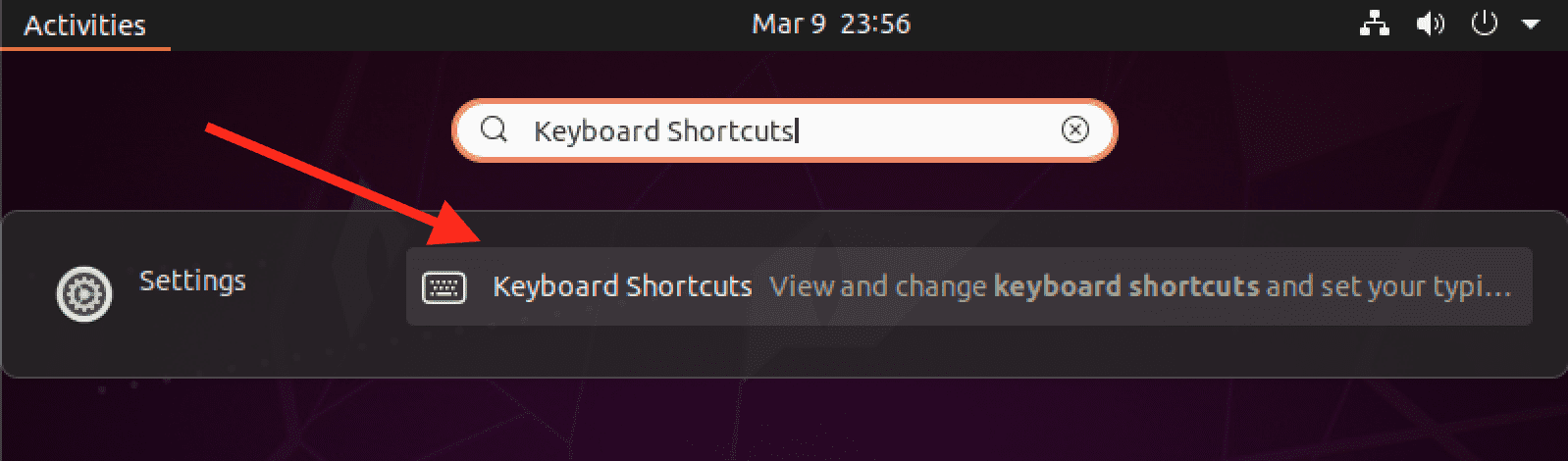
Step 1. Open the Keyboard Shortcuts Settings
Press the Super key (also known as the Windows key) on your keyboard and type “Keyboard Shortcuts”. Click on the Keyboard Shortcuts app that appears in the search results.
Keyboard Shortcuts
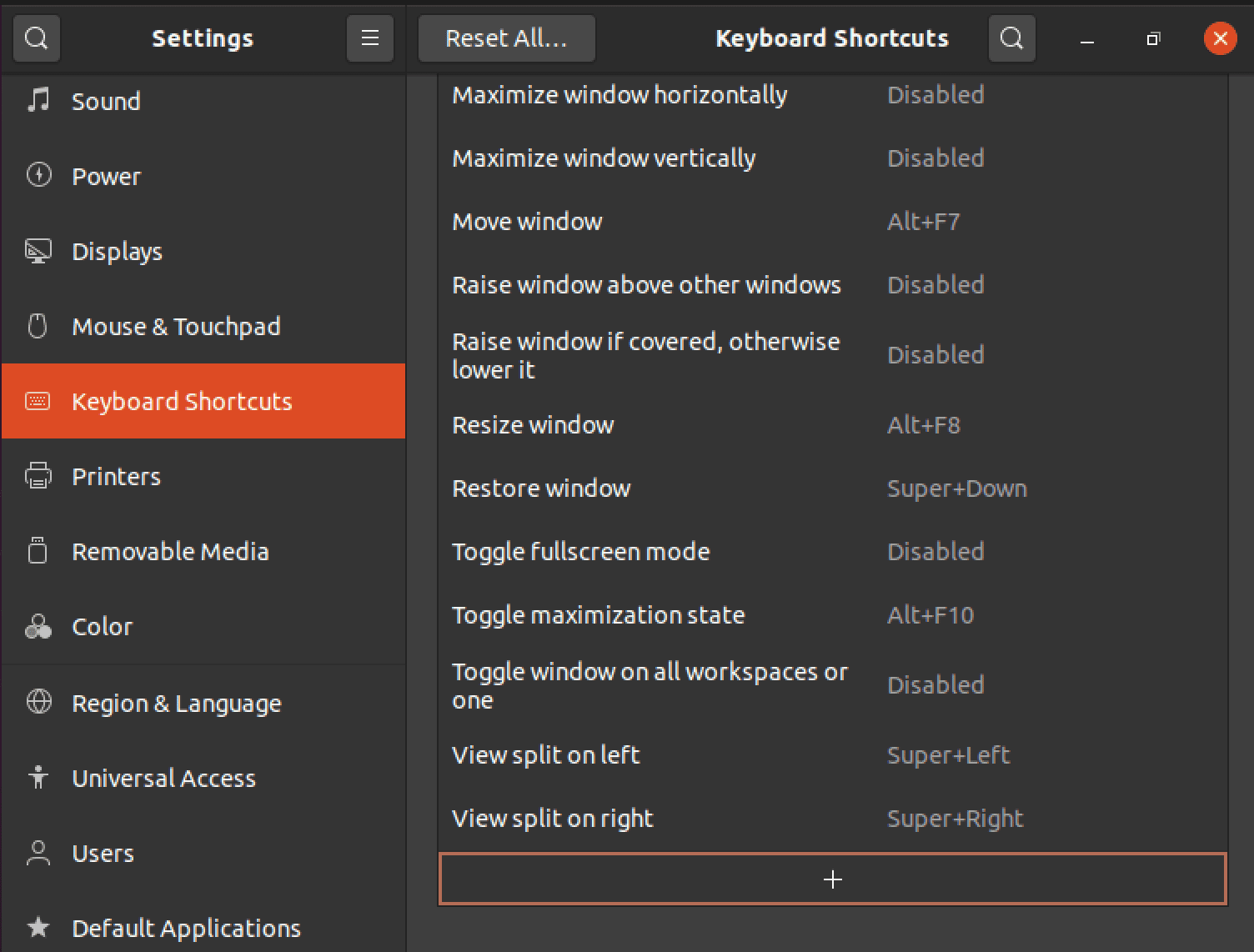
Step 2. Click on the Plus (+) Button
The keyboard shortcut window should look similar to the image below. Now, scroll to the bottom and click the plus (+) button. This will bring up a new dialog where you can enter the details of your custom shortcut.
Add a shorcut
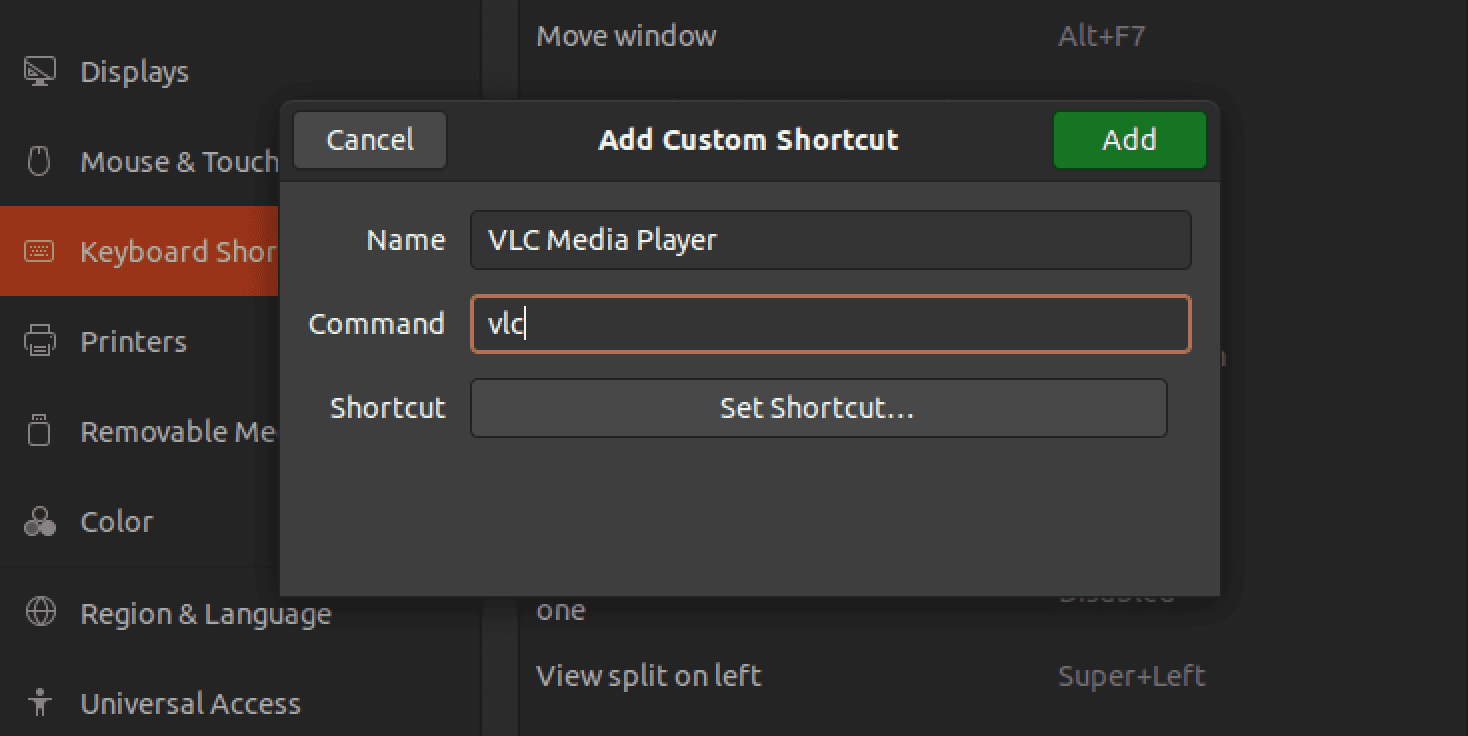
Enter the name and command for your custom shortcut: In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for your shortcut. In the Command field, enter the command you want to run when you use the shortcut. For example, if you want to launch the Terminal with the shortcut, you would enter “gnome-terminal” (without the quotes) in the Command field. For this post, we will create a keyboard shortcut to launch the VLC media player.
Step 3. Assign a Keyboard Shortcut
Click on the Set Shortcut button and press the keys you want to use for your custom shortcut.
Create VLC shortcut
Next, you will need to press the keys that you want to use for your shortcut. For this post, we will use the keyboard combination, Ctrl + W + V to open VLC. If the keys are already assigned to another shortcut, you’ll be asked if you want to reassign them. If you do, click on the Reassign button.
Step 4. Save Your Custom Shortcut
Click on the Add button to save your new custom shortcut.
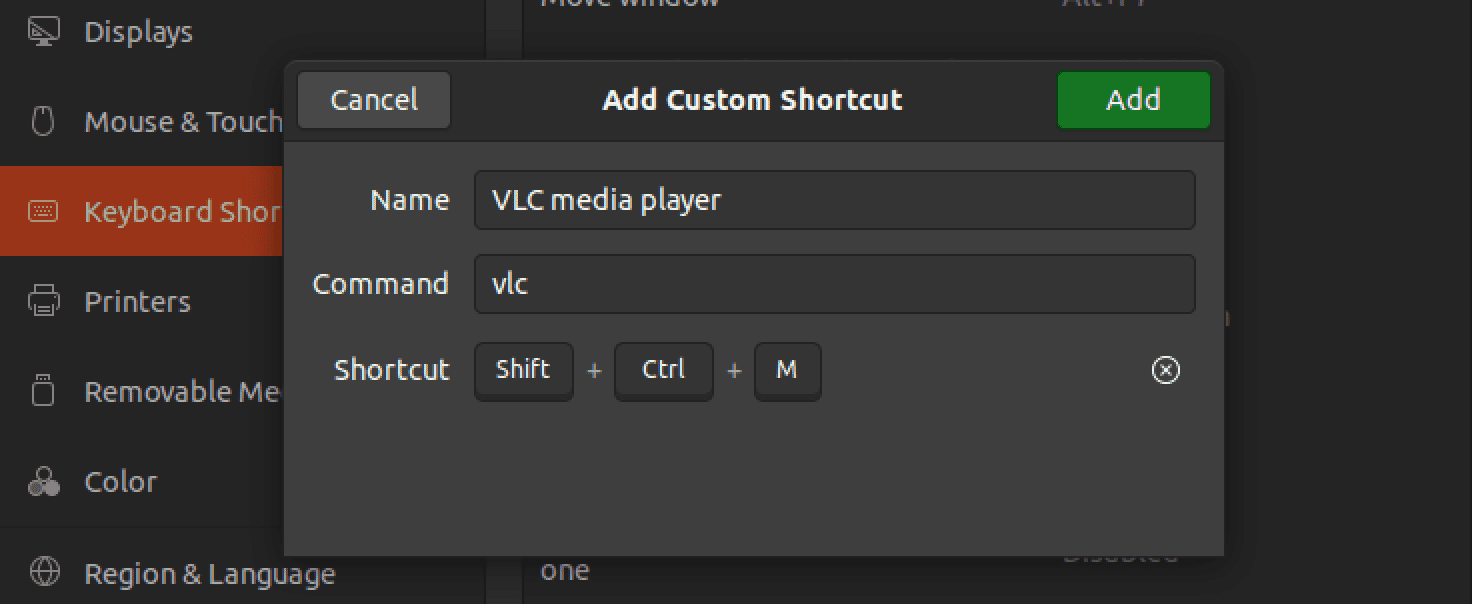
VLC shortcut
Step 5. Test your Custom Shortcut
Press the keys you assigned to your custom shortcut and make sure it works as expected.
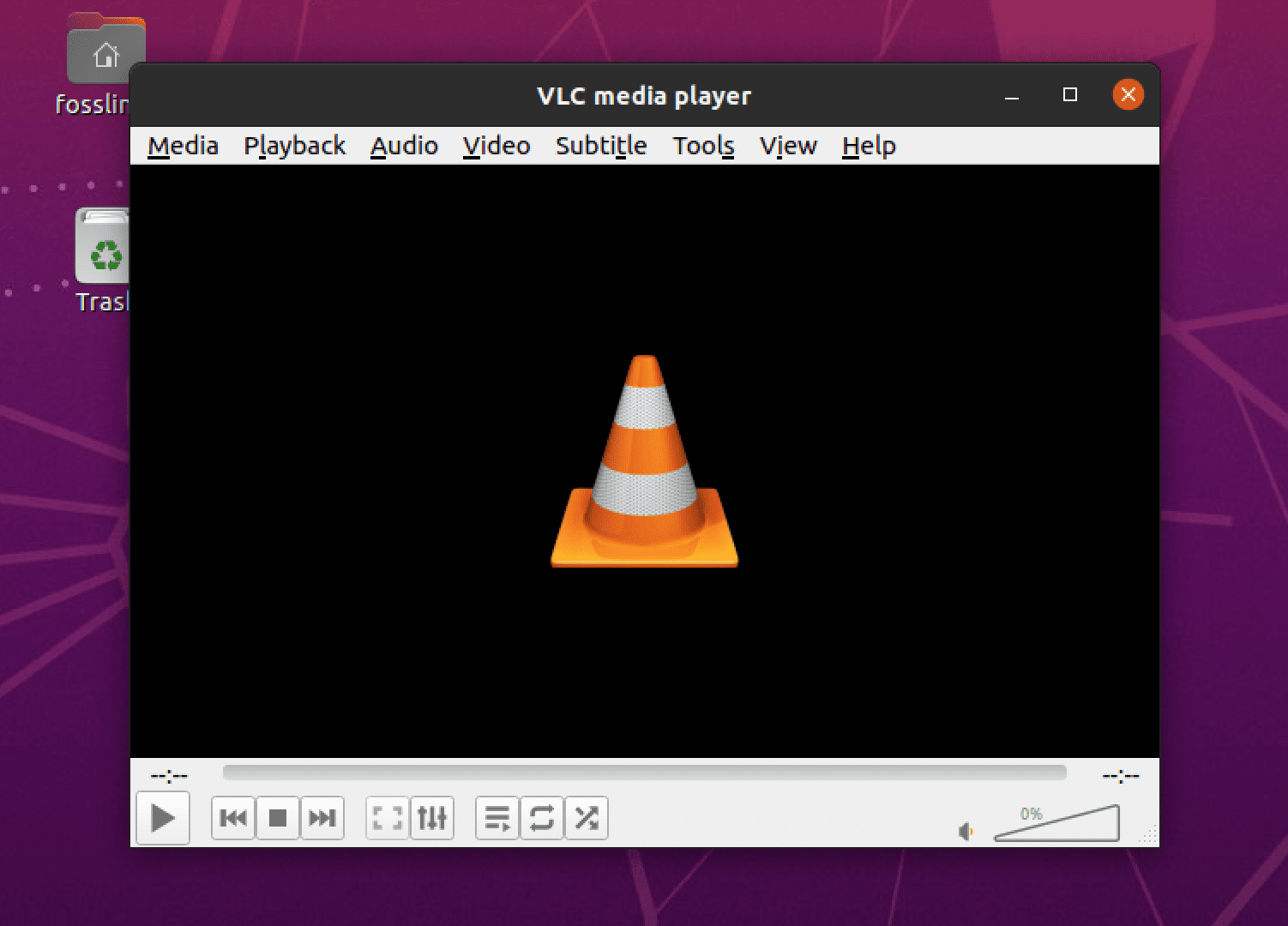
VLC
That’s it! You’ve successfully created a custom keyboard shortcut on Ubuntu. You can repeat the process to create as many custom shortcuts as you like.
Conclusion
Ubuntu keyboard shortcuts are an efficient way to navigate and work on your Ubuntu system. These shortcuts make it easier and quicker to perform common tasks, such as opening a new tab, switching between tabs, moving the cursor, or deleting text. It’s important to understand the role of the Super key in executing many of the most useful keyboard shortcuts in Ubuntu.
By mastering these shortcuts, you can streamline your workflow, increase your productivity and enjoy the full power of the Ubuntu operating system. Remember to create your own custom keyboard shortcuts to make the experience even more personalized to your needs.