Hello, FOSSLinux readers! Over the years, I have explored and experimented with several Linux distributions and have found them to be immensely useful and flexible. However, among all the Linux distributions, Linux Mint has particularly caught my attention due to its user-friendly interface, stability, and efficiency. It has quickly become one of my favorites.
Nonetheless, as with any software, keeping it up-to-date is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Therefore, in this guide, I will provide you with a step-by-step tutorial on how to set up automatic updates in Linux Mint, making it easier and more convenient for you to keep your system updated.
Let’s dive right in!
Why automatic updates matter
Before we proceed, let’s discuss the importance of automatic updates. You might wonder, “Why bother?” Well, here are a few reasons:
- Security: Regular updates patch vulnerabilities, ensuring your system stays protected.
- Stability: Updates often fix bugs, enhancing system stability.
- Enhanced features: Newer versions sometimes come with additional features or improvements over the old ones.
- Peace of mind: Once set, you would not have to remember to update your system manually.
Personally, I’ve always been an advocate of staying updated. It’s like giving your system a fresh coat of paint periodically. But I also understand that remembering to do it manually can be a chore. That’s where automatic updates come in handy.
Getting started with Linux Mint’s Update Manager
Linux Mint comes equipped with its built-in tool called Update Manager. It’s your one-stop-shop for all things related to updates.
- Launching the Update Manager: Click on the Menu and search for “Update Manager”. When it appears, click on it.
- Reviewing available updates: When the Update Manager opens, it will present a list of available updates. It’s good to occasionally check this manually, just to understand what’s being updated.
- Setting preferences: Before enabling automatic updates, you need to set your preferences. Click on ‘Edit’ in the top menu and select ‘Preferences’. This is where the magic happens.
Linux Mint Update Manager
Configuring automatic updates
In the Preferences window, you will find various settings. Here’s how to configure them for automatic updates:
- Automated refresh: Here, you can choose how often the Update Manager checks for updates. I set mine to daily because I like my system to stay as current as possible. However, if you don’t want daily checks, weekly is a good compromise.
- Auto-upgrade: This is where you enable automatic updates. Choose ‘Apply updates automatically’.
- Level of updates: Linux Mint categorizes updates based on levels. While some updates are absolutely safe and tested, others might be a bit riskier. You can choose which levels you’re comfortable updating automatically. Personally, I stick to levels 1 and 2 for automatic updates. They are well-tested and seldom cause issues.
- Security updates: Always ensure that security updates are applied automatically. You don’t want to lag behind on these!
- Kernel updates: This one’s a bit tricky. Kernels are the heart of your operating system. While updating them can bring improvements, it can sometimes lead to issues. I prefer to handle kernel updates manually. It gives me a chance to read about the update and ensure it’s stable. However, if you’re feeling adventurous, you can opt for automatic kernel updates.
- Other settings: There are other settings like blacklisting certain updates, notification settings, etc. Tweak these based on your preferences.
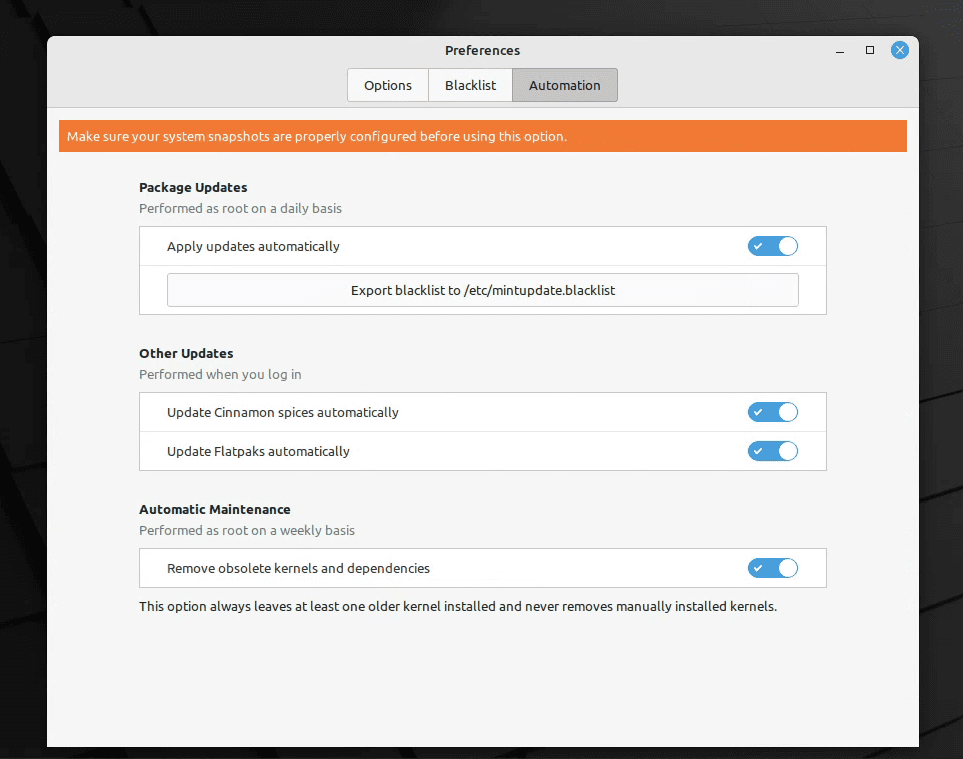
Enabling automatic updates in Linux Mint
Once you’re happy with your settings, click ‘OK’.
Monitoring and handling issues
Setting up automatic updates is pretty straightforward, but it’s also essential to be prepared in case something goes wrong. Here’s what you can do:
- Manual checks: Even with automatic updates, I recommend manually opening the Update Manager once in a while. It gives you an idea of what’s being updated and helps you catch potential issues.
- Backup, Backup, Backup: Cannot stress this enough. Always have a backup of your important data. Tools like Timeshift in Linux Mint make this easy.
Troubleshooting Automatic Updates in Linux Mint
Even with the best configurations, there may be times when you run into issues with automatic updates. Here’s a quick guide on troubleshooting some common problems:
Updates not being applied automatically: If you notice that updates aren’t being installed:
- Ensure that the Update Manager isn’t paused or stopped.
- Check your internet connection. A stable connection is essential for updates.
- Confirm your update preferences in the Update Manager to ensure they’re set correctly.
System instability after an update: Rarely, an update might cause system issues.
- Boot into recovery mode and use Timeshift to revert to a previous system snapshot.
- If you identified a problematic update, consider blacklisting it so it won’t be applied automatically in the future.
Update Manager not launching: If you find the Update Manager not launching:
- Restart your computer. Often, a simple restart can fix a multitude of problems.
- Try launching the Update Manager from the terminal using
mintupdate. This could provide clues if there are any errors.
Notification issues: If you’re not receiving notifications about updates:
- Double-check the notification settings in the Update Manager preferences.
- Ensure that the system’s notification daemon is running.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Automatic Updates in Linux Mint
Why do some updates show a warning sign next to them?
- These updates usually belong to a higher level and might be potentially riskier. Linux Mint categorizes updates to help users understand the implications.
Can I revert an update if it causes issues?
- Absolutely! Timeshift is a fantastic tool in Linux Mint that allows you to take system snapshots. If an update causes trouble, you can revert to a previous state using Timeshift.
How can I stop certain updates from being installed?
- You can blacklist specific updates in the Update Manager. This ensures that they won’t be installed automatically.
Do automatic updates also upgrade to a new version of Linux Mint?
- No, automatic updates apply patches to your current version. Upgrading to a newer version of Linux Mint is a separate process and is typically done manually.
I prefer manual updates. Is it okay not to use automatic updates?
- While automatic updates offer convenience and ensure you’re always up-to-date, manual updates give you more control. It’s a matter of personal preference. If you choose manual updates, make sure you remember to check and apply them regularly.
Conclusion
One of the most appealing features of Linux Mint is its ability to provide an effortless and user-friendly experience when it comes to installing updates. By enabling automatic updates, the process becomes even smoother and easier to manage. This means that you can stay on top of the latest improvements and security patches without any additional effort. As someone who has been using this feature for years, I can confidently say that it is both efficient and effective. However, it is always prudent to have a backup and stay informed, even when using automatic updates.

