For any Linux enthusiast, terminal utilities form an indispensable portion of their toolkit. These are mighty tools that offer efficient control and observation of your system, thereby, ramping up productivity levels. This tutorial discusses the installation process for three such terminal utilities; namely, htop, Neofetch, and Tmux. These utilities enjoy immense popularity amongst the Linux audience and we’re thrilled to guide you on installing them on Fedora.
Why these utilities?
Before we delve into the installation steps, it’s important to understand the reasons for using these tools. htop acts as an engaging system-monitor viewer that offers a more digestible and understandable display compared to the conventional top command. Neofetch, on another note, presents system details in a vibrant and captivating manner, making it a delightful enhancement to any terminal. Tmux, conversely, is a terminal multiplexer permitting the control of multiple terminal activities from just one window. It proves to be extremely beneficial for juggling multiple tasks or managing several remote sessions.
Installing htop on Fedora
Htop is one of those tools that I can’t live without. It gives a detailed overview of the system processes, and its colorful interface makes it easy to read at a glance.
How to install
Installing htop on Fedora is straightforward, thanks to the Fedora repositories. Simply open your terminal and run the following command:
sudo dnf install htop
This command will prompt you for your password, and then it will proceed to install htop on your system.
Example output on Fedora 38:
[fosslinux@fedora ~]$ sudo dnf install htop [sudo] password for fosslinux: Sorry, try again. [sudo] password for fosslinux: Last metadata expiration check: 2:58:08 ago on Mon 11 Mar 2024 12:26:35 PM EDT. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: htop x86_64 3.3.0-1.fc38 updates 200 k Installing dependencies: hwloc-libs x86_64 2.10.0-1.fc38 updates 2.1 M Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 2 Packages Total download size: 2.3 M Installed size: 3.3 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/2): htop-3.3.0-1.fc38.x86_64.rpm 410 kB/s | 200 kB 00:00 (2/2): hwloc-libs-2.10.0-1.fc38.x86_64.rpm 2.7 MB/s | 2.1 MB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1.7 MB/s | 2.3 MB 00:01 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : hwloc-libs-2.10.0-1.fc38.x86_64 1/2 Installing : htop-3.3.0-1.fc38.x86_64 2/2 Running scriptlet: htop-3.3.0-1.fc38.x86_64 2/2 Verifying : htop-3.3.0-1.fc38.x86_64 1/2 Verifying : hwloc-libs-2.10.0-1.fc38.x86_64 2/2 Installed: htop-3.3.0-1.fc38.x86_64 hwloc-libs-2.10.0-1.fc38.x86_64 Complete!
Using htop
To use htop, just type htop in your terminal and press Enter. You’ll be greeted with a detailed view of your system’s processes. You can navigate using your keyboard arrows and perform actions using function keys.
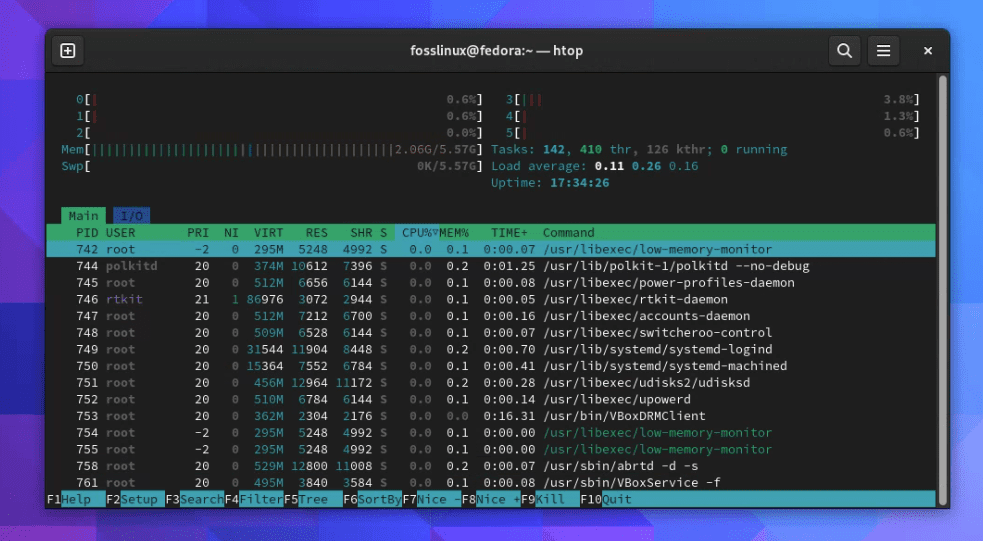
Running Htop on Fedora 38
How to uninstall
If, for some reason, you decide htop is not for you (though I’d find that surprising), you can uninstall it with:
sudo dnf remove htop
Installing Neofetch on Fedora
Neofetch is a utility I have a love-hate relationship with. I love it for its ability to showcase my system info with flair, but I sometimes find it a bit too flashy for my taste. Regardless, it’s a fantastic tool for spicing up screenshots or just bragging about your system specs.
How to install
To install Neofetch on Fedora, run:
sudo dnf install neofetch
Example output:
[fosslinux@fedora ~]$ sudo dnf install neofetch [sudo] password for fosslinux: Last metadata expiration check: 3:07:55 ago on Mon 11 Mar 2024 12:26:35 PM EDT. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: neofetch noarch 7.1.0-9.fc38 fedora 89 k Installing dependencies: catimg x86_64 2.7.0-8.fc38 fedora 55 k gc x86_64 8.2.2-3.fc38 fedora 110 k gdk-pixbuf2-xlib x86_64 2.40.2-6.fc38 fedora 57 k imlib2 x86_64 1.7.4-4.fc38 fedora 236 k libXxf86dga x86_64 1.1.5-10.fc38 fedora 20 k perl-NKF x86_64 1:2.1.4-28.fc38 fedora 144 k toilet x86_64 0.3-14.fc38 fedora 730 k w3m x86_64 0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38 fedora 1.1 M Installing weak dependencies: caca-utils x86_64 0.99-0.69.beta20.fc38 updates 98 k w3m-img x86_64 0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38 fedora 23 k xdpyinfo x86_64 1.3.3-3.fc38 fedora 26 k xrandr x86_64 1.5.2-2.fc38 fedora 46 k xwininfo x86_64 1.1.5-6.fc38 fedora 32 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 14 Packages Total download size: 2.8 M Installed size: 5.9 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/14): catimg-2.7.0-8.fc38.x86_64.rpm 215 kB/s | 55 kB 00:00 (2/14): gdk-pixbuf2-xlib-2.40.2-6.fc38.x86_64.r 218 kB/s | 57 kB 00:00 (3/14): gc-8.2.2-3.fc38.x86_64.rpm 416 kB/s | 110 kB 00:00 (4/14): libXxf86dga-1.1.5-10.fc38.x86_64.rpm 244 kB/s | 20 kB 00:00 (5/14): neofetch-7.1.0-9.fc38.noarch.rpm 525 kB/s | 89 kB 00:00 (6/14): imlib2-1.7.4-4.fc38.x86_64.rpm 1.1 MB/s | 236 kB 00:00 (7/14): perl-NKF-2.1.4-28.fc38.x86_64.rpm 1.0 MB/s | 144 kB 00:00 (8/14): w3m-img-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_6 314 kB/s | 23 kB 00:00 (9/14): xdpyinfo-1.3.3-3.fc38.x86_64.rpm 194 kB/s | 26 kB 00:00 (10/14): toilet-0.3-14.fc38.x86_64.rpm 2.3 MB/s | 730 kB 00:00 (11/14): xrandr-1.5.2-2.fc38.x86_64.rpm 354 kB/s | 46 kB 00:00 (12/14): xwininfo-1.1.5-6.fc38.x86_64.rpm 241 kB/s | 32 kB 00:00 (13/14): w3m-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64.r 2.1 MB/s | 1.1 MB 00:00 (14/14): caca-utils-0.99-0.69.beta20.fc38.x86_6 173 kB/s | 98 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 1.3 MB/s | 2.8 MB 00:02 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : xwininfo-1.1.5-6.fc38.x86_64 1/14 Installing : xrandr-1.5.2-2.fc38.x86_64 2/14 Installing : toilet-0.3-14.fc38.x86_64 3/14 Installing : perl-NKF-1:2.1.4-28.fc38.x86_64 4/14 Installing : libXxf86dga-1.1.5-10.fc38.x86_64 5/14 Installing : xdpyinfo-1.3.3-3.fc38.x86_64 6/14 Installing : imlib2-1.7.4-4.fc38.x86_64 7/14 Installing : caca-utils-0.99-0.69.beta20.fc38.x86_64 8/14 Installing : gdk-pixbuf2-xlib-2.40.2-6.fc38.x86_64 9/14 Installing : gc-8.2.2-3.fc38.x86_64 10/14 Installing : w3m-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 11/14 Installing : w3m-img-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 12/14 Installing : catimg-2.7.0-8.fc38.x86_64 13/14 Installing : neofetch-7.1.0-9.fc38.noarch 14/14 Running scriptlet: neofetch-7.1.0-9.fc38.noarch 14/14 Verifying : catimg-2.7.0-8.fc38.x86_64 1/14 Verifying : gc-8.2.2-3.fc38.x86_64 2/14 Verifying : gdk-pixbuf2-xlib-2.40.2-6.fc38.x86_64 3/14 Verifying : imlib2-1.7.4-4.fc38.x86_64 4/14 Verifying : libXxf86dga-1.1.5-10.fc38.x86_64 5/14 Verifying : neofetch-7.1.0-9.fc38.noarch 6/14 Verifying : perl-NKF-1:2.1.4-28.fc38.x86_64 7/14 Verifying : toilet-0.3-14.fc38.x86_64 8/14 Verifying : w3m-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 9/14 Verifying : w3m-img-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 10/14 Verifying : xdpyinfo-1.3.3-3.fc38.x86_64 11/14 Verifying : xrandr-1.5.2-2.fc38.x86_64 12/14 Verifying : xwininfo-1.1.5-6.fc38.x86_64 13/14 Verifying : caca-utils-0.99-0.69.beta20.fc38.x86_64 14/14 Installed: caca-utils-0.99-0.69.beta20.fc38.x86_64 catimg-2.7.0-8.fc38.x86_64 gc-8.2.2-3.fc38.x86_64 gdk-pixbuf2-xlib-2.40.2-6.fc38.x86_64 imlib2-1.7.4-4.fc38.x86_64 libXxf86dga-1.1.5-10.fc38.x86_64 neofetch-7.1.0-9.fc38.noarch perl-NKF-1:2.1.4-28.fc38.x86_64 toilet-0.3-14.fc38.x86_64 w3m-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 w3m-img-0.5.3-60.git20230121.fc38.x86_64 xdpyinfo-1.3.3-3.fc38.x86_64 xrandr-1.5.2-2.fc38.x86_64 xwininfo-1.1.5-6.fc38.x86_64 Complete!
Using Neofetch
Running Neofetch is as simple as typing neofetch in your terminal. It will display your system information along with your operating system logo in ASCII art.
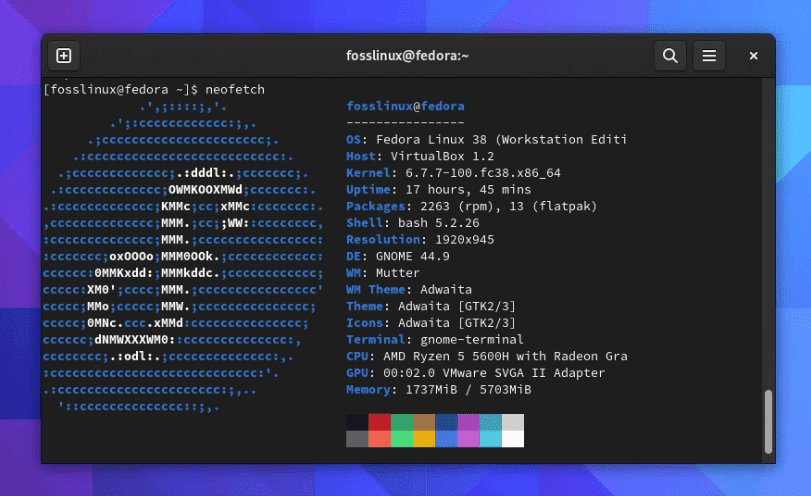
Running Neofetch on Fedora 38
How to uninstall
If Neofetch doesn’t suit your fancy, you can remove it with:
sudo dnf remove neofetch
Installing Tmux on Fedora
Tmux is a game-changer for me. It allows me to have multiple terminal sessions in one window, saving me from the clutter of multiple terminal windows.
How to install
Installing tmux on Fedora is done by running:
sudo dnf install tmux
Example output:
[fosslinux@fedora ~]$ sudo dnf install tmux Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:45 ago on Mon 11 Mar 2024 03:40:14 PM EDT. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Architecture Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: tmux x86_64 3.3a-3.fc38 fedora 508 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 508 k Installed size: 1.2 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: tmux-3.3a-3.fc38.x86_64.rpm 710 kB/s | 508 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 563 kB/s | 508 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : tmux-3.3a-3.fc38.x86_64 1/1 Running scriptlet: tmux-3.3a-3.fc38.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : tmux-3.3a-3.fc38.x86_64 1/1 Installed: tmux-3.3a-3.fc38.x86_64 Complete!
Using Tmux
To start using tmux, simply type tmux in your terminal. You can create new windows with Ctrl+b c and switch between them with Ctrl+b n (for next window) or Ctrl+b p (for previous window). There’s a lot more to tmux, so I recommend checking out its manual page (man tmux) for more commands.

Running tmux on Fedora 38
How to uninstall
If tmux isn’t your cup of tea, you can uninstall it with:
sudo dnf remove tmux
Conclusion
There you have it, a simple guide to installing htop, Neofetch, and tmux on Fedora. These utilities have become a part of my daily workflow, and I highly recommend giving them a try.

1 comment
lscpu | lolcat | htop -20
instead of neofetch?