In today’s Terminal Tuts session, we shall show you several ways of creating and editing text files that can be done easily and quickly using the command line.
Here are the following commands that can be used to create a text file.
- Cat command
- Touch command
- Standard Redirect Symbol
- Nano command
- Vi command
1. Cat Command
Cat command is mainly used to preview the text file content. However, you can use it to create new files and edit them, too, by using the redirection method. For example, use the following command to create a new file:
cat > cattestfile.txt
After executing the command, a cursor will appear waiting for you to enter any text you need to edit the newly created file.
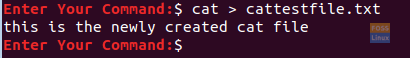
Cat Command
Once you finished editing your file and you need to exit, press CTRL+D. Now you can see the standard command prompt comes again.
To check if the file was created successfully, you can use the list command as follows:
ls -l
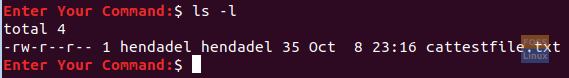
Check Newly Created File
To ensure that the text you have entered was saved successfully, then you can use the command:
cat cattestfile.txt
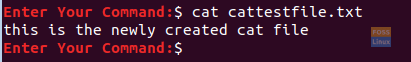
Display The Cat File Content
2. Touch Command
In this method, you will be able to create single or multiple files using the touch command.
To create a single file.
touch touchfile.txt
Touch Command
To check if the new file was created successfully.
ls -l
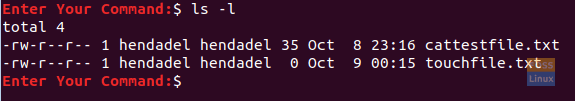
Touch File
Now, in case you need to create multiple files. Then you can use the following command.
touch file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt file4.txt
Touch Command
To check if the previous files were created or not.
ls -l
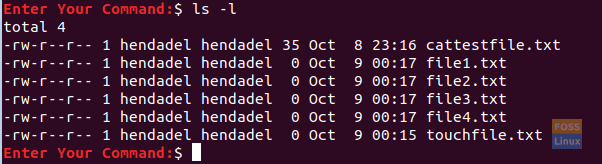
Check Newly Created Multiple Touch File
3. Redirect command
In this method, we will use the standard redirect command to create a new file. Unlike the touch command, this method will be able to create one single file only at the time.
To create a new file.
> stdred.txt
Standard Redirect Symbol
To check that the file was created successfully.
ls -l
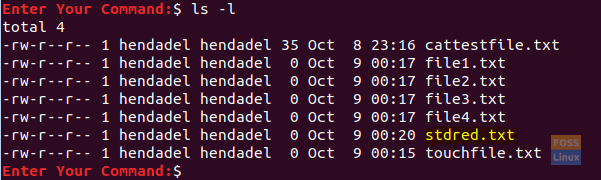
Standard Redirect Symbol
4. Nano Command
Using the nano command, you will be able to create a new file and edit it too.
To create a new file.
nano nanofile.txt
Nano Command
A nano editor will open like the below screenshot, and you will be able to write and edit your file. Once you have finished editing your file, use the CTRL+O to save your file and use the CTRL+X to exit the nano editor.
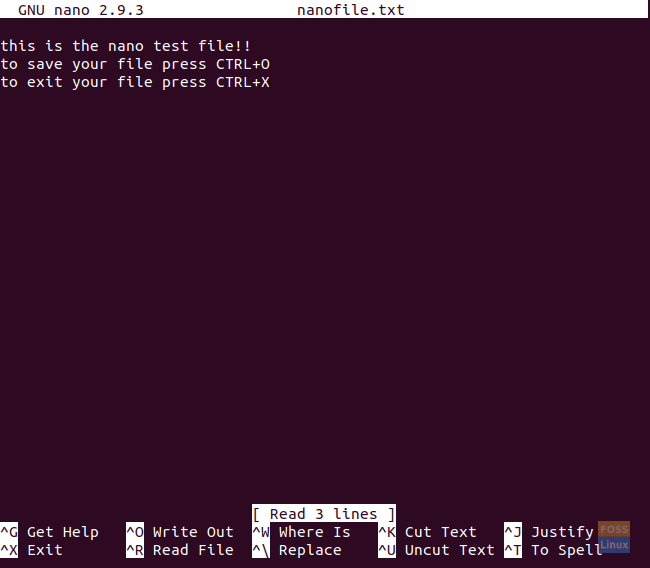
Edit The Newly Created Nano File
To ensure that the previous file was created successfully, use the list command.
ls -l
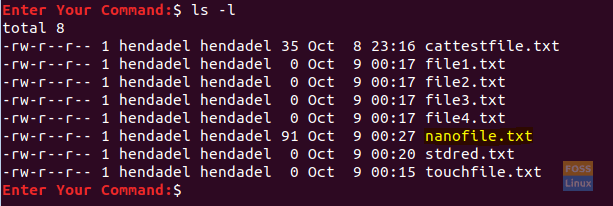
Nano Command
To display the file content, use the following command.
cat nanofile.txt
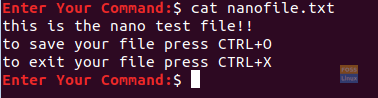
Display The Nano File Content
6. Vi Command
In this method, we will use the vi command to create a new file and edit it.
To create a new file.
vi vifile.txt
Vi Editor
A vi editor will open then you can start editing your file. Vi is a little bit different than the nano editor, which means for every action you need to do, there is a command that you need to execute first. For example, if you need to enter the vi command mode first you need to press ESC, then one of the following commands:
:i --> To insert a new line. :w --> To save file. :q --> To exit file. :wq --> To save and quit file. :q! --> To exit file without saving .
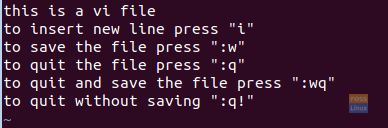
Vi Editor
To check if the file was created successfully.
ls -l
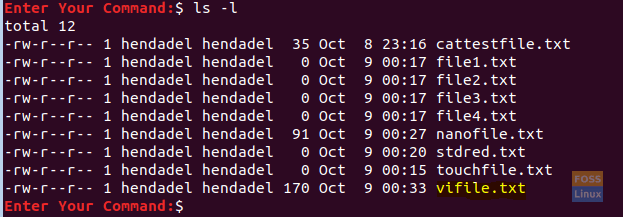
Vi Command
To display the file content.
cat vifile.txt
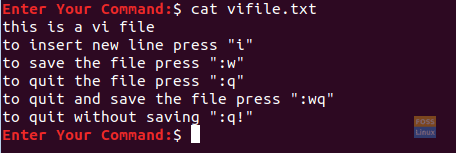
Display The Vi File Content
Conclusion
That ends our guide on creating text files and editing them using command-lines via the Linux Terminal. I hope you enjoyed it.

