Smartphone systems can be used through a computer system to some extent. You can always use Android emulators, or virtual devices, or even Android for x86 architecture systems, but what about your very own phone? How would you use the interface of your Android phone through your computer?
Well, this is where we introduce Scrcpy.
Control Android device from a Linux PC
Scrcpy is a desktop program that can be used to access your Android phone’s system and interface through your computer. The app is quite convenient, and some of its best features are highlighted below.
Interface
The user interface is purposefully minimal. There is nothing more to the window than merely the area where the connected phone’s interface can be seen. There are several command-line options available for configuration, balancing out the absence of graphical options for setup. The command-line options are simple enough and very extensive.
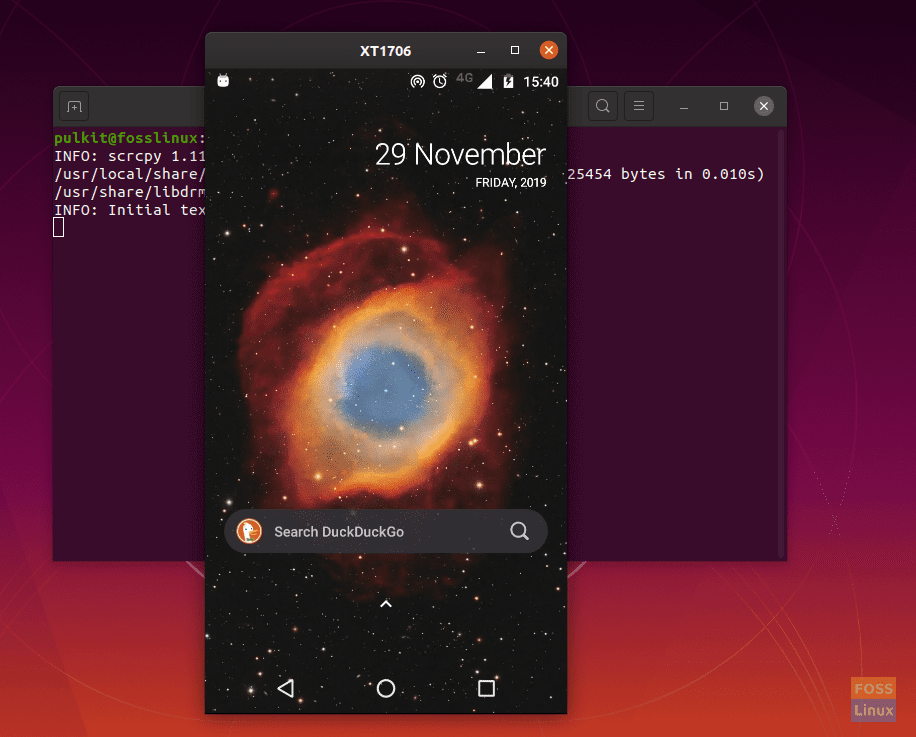
Interface
Basic features
As said before, the program focuses on being minimal and light. This ensures comparatively faster and snappier motions in the program. The performance range stays between 30 and 60 FPS (frames per second).
The resolution of the display starts from 1920×1080 or above. The startup and latency period is very low. Being 35-70ms for latency, and less than a second to show the first view of the interface window.
One of the most attractive features is the non-intrusiveness. There is nothing installed, and nothing left behind on the phone’s system, so you can be assured that your data is safe on the other side of the interface.
Launch options
There are a lot of options available. Some of them are useful for optimization, and some can come in handy while using the program.
To be clear, these options are to be used on the Terminal in the following way:
For example, the option is ‘-b,’ the syntax will be:
scrcpy -b
Bitrate
The bitrate of the stream can be configured. The default being 8MB/s, you can set it to the desired rate using the following command:
Example: Changing it to 10MB/s
scrcpy -b 10M
Cropping window size
The default size will be the actual resolution of your phone. You can crop the window using a simple command. The value to be entered is only one (the height), and the width will be configured according to the ratio of your phone display. For example, if you want to launch the window at 1024 pixels height, use the command in the following manner:
scrcpy -m 1024
This sets the maximum height of the window as 1024 px. Of course, you cannot go beyond the maximum resolution of the phone that you own.
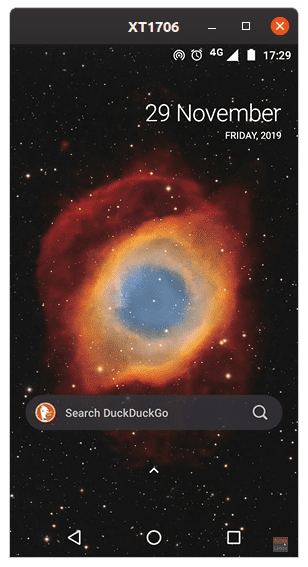
Smaller window size.
TIP: Smaller window size accompanies a faster performance.
Fullscreen
A simple -f option deploys the app in the fullscreen mode.
scrcpy -f
Read-only mode
In case you don’t want your phone to be tampered with, or want to be on the safe side while using this program, you can employ the read-only mode, which allows the usage of the system, but not creation, editing or deletion of files on the system. To use this option, issue the following command:
scrcpy -n
Recording
One of the most (and most used) features of this program is the ability to record the display of the connected phone for the duration that the program is running. To start the program with the recording on, you need to use the -r option, followed by the name for the file, by which name the video will be saved. Example:
scrcpy -r video_test.mp4
NOTE: It is essential to know that only .mp4 and .mkv extensions can be used for this purpose.
Turning screen off
To save the battery of your phone, and if you are going to use the app for a prolonged period, you should use this option, which causes the display of the phone to turn blank, but you will still see the interface on your computer screen. To use this option, use the following command:
scrcpy -S
Show touches
An option can be used to show touches on the interface. If you’re recording a video for a tutorial or showing something to someone, this option can be rather useful. To use this option, enter the following command:
scrcpy -t
Window title
You can even add a custom title to the app window. To use this option, enter this command:
scrcpy --window-title text
Where ‘text‘ is the desired title.
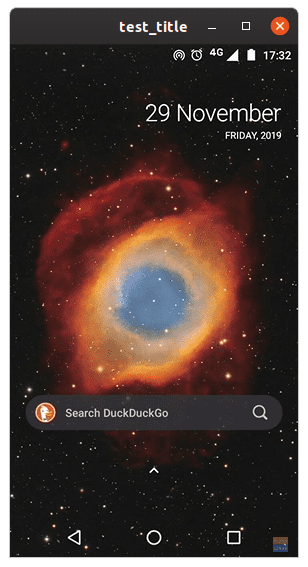
Custom window title.
Installing apps
We think this is one of the best features of the program. While using Scrcpy, if you drag and drop an APK file on the window, the app will get installed on the phone.
For the case of Android phone enthusiasts, we love to experiment with new apps, and often, we download it on our computers. Or say, your phone has no internet access (maybe due to malfunction), but your laptop does, and you need to install an app/service to fix it. Sure, you can transfer and then install it, or use ADB for the purpose, but nothing can be easier than dragging and dropping.
Keyboard shortcuts
There are several useful keyboard shortcuts. These can be used after you’ve launched the window, unlike the command-line options, which can only be used at the time of launching. Here’s a list of the useful keyboard shortcuts:
| Purpose | Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Switch to fullscreen | CTRL + F |
| Click on home | CTRL + H Middle click |
| Click on back | CTRL + B Right Click |
| Click on app-switch button | CTRL + S |
| Click on menu | CTRL + M |
| Volume up | CTRL + UP |
| Volume down | CTRL + DOWN |
| Click on power | CTRL + P |
| Turn phone screen off, but keep it running on mirroring | CTRL + O |
| Expand notification panel | CTRL + N |
| Collapse notification panel | CTRL + SHIFT + N |
| Copy device clipboard to computer | CTRL + C |
| Paste computer clipboard to device | CTRL + V |
| Copy computer clipboard to device | CTRL + SHIFT + V |
Installation
Installation of Scrcpy on Ubuntu is straightforward, as the program is available to be installed through Ubuntu Software. Enter Ubuntu Software, search for ‘scrcpy,’ and you’ll find the program.
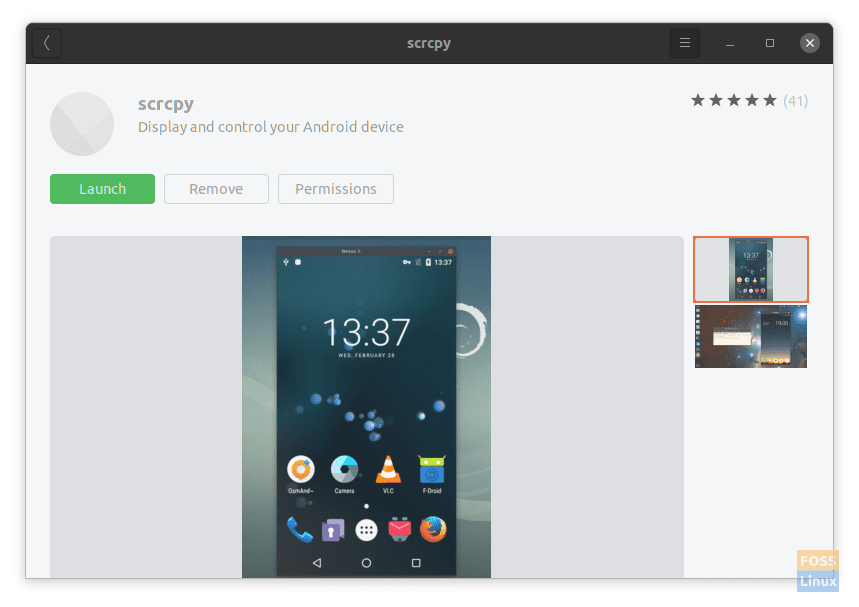
Scrcpy on Ubuntu
There is also a Snap package. So, you can install Snap on your system, which allows you to not only install this but many other Linux programs.
To install Snap, use the following command on Debian/Ubuntu and their derivatives:
sudo apt-get install snapd
On Fedora:
sudo dnf install snapd
If you have any other distribution, follow this link to your OS’s page, to install snapd. After that, to install Scrcpy, enter:
sudo snap install scrcpy
Otherwise, if you want to download the build file from GitHub.
How to use Scrcpy
Before launching the program itself, you will need to set up your phone to support the process. Enter Developer Settings on your phone, and enable ‘USB Debugging.’ After that, connect your phone to your system with a data cable. There will be a prompt of whether you want your phone to trust the system that is linked. Tap on the favorable option.
To launch Scrcpy after setting up the phone, enter in the command line:
scrcpy
You can also use the options that we have written about in the former part of this article.
Wireless connection
To establish the connection wirelessly, you will need to install ADB (Android Debug Bridge), which allows you to modify packages and features of your Android phone through your computer. Here’s a guide for the installation and ADB setup on Linux PC.
After completing the command of this form:
adb connect <IP ADDR OF PHONE>:5555
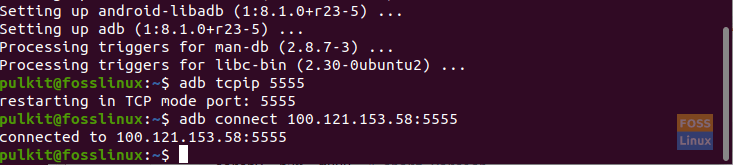
Enabling wireless connection.
Run this command:
scrcpy
Conclusion
Scrcpy, although seeming minimal and bland, is extremely feature-filled. If you add the capabilities it could possess in conjunction with other programs (like ADB), you will have access to an even more significant number of possibilities.


1 comment
A little help please? Command NOT found.
angel@Emerald:~$ sudo snap install scrcpy
snap “scrcpy” is already installed, see ‘snap help refresh’
angel@Emerald:~$ scrcpy
No command ‘scrcpy’ found, did you mean:
Command ‘scrapy’ from package ‘python-scrapy’ (universe)
scrcpy: command not found