If you have been wondering how to get the basic task such as formatting an external hard disk, USB disk, SD card, or Micro-SD cards on Linux, you are not alone.
There is no direct GUI method to format the hard disk. It is simpler to perform formatting within MS Windows Explorer. Although Ubuntu and the elementary OS come with ‘Files’ that offers similar functionality to the Windows File Explorer, it doesn’t have a format feature.
Thankfully, in Linux, you get the best of the software for free. Also, there is a Command-line way of doing things that are lightning-fast than any other method. For the GUI scenario, I would recommend using the GParted app. It is a free and open source software (FOSS) and is very powerful in terms of features and what it can do. Since we are discussing formatting the hard disk, let’s see how you can format a storage media to almost any format you need.
Format Storage Media in Ubuntu and elementary OS
METHOD 1: Using GParted software
Step 1: Install GParted: GParted is available in the ‘Software Center’ of Ubuntu and elementary OS. Look for ‘GParted’ and install it. Alternatively, you can use apt-get in the terminal to install it.
sudo apt-get install gparted
Step 2: Launch the program from ‘Applications’.
Step 3: Plugin the storage media which you want to format.
Step 4: Right-click on the drive which you want to format and select the desired format. Typically, most USB drives use FAT32 format, and Windows-based external hard disks use NTFS. Linux can read any of these formats.
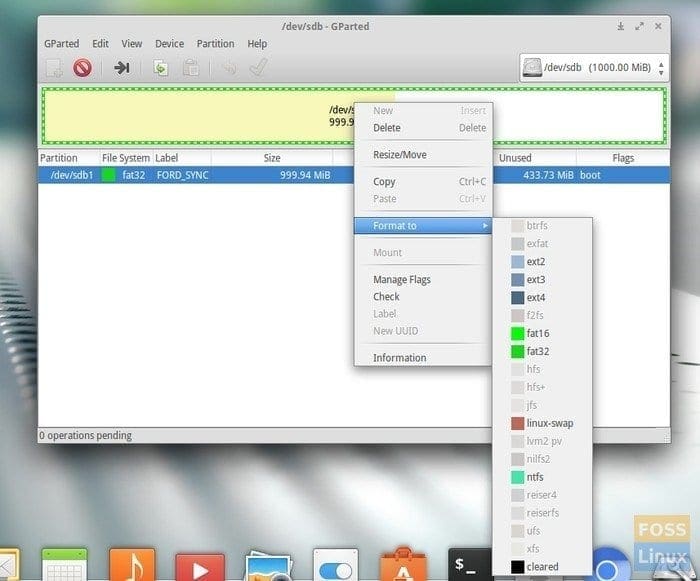
GParted Format Options
Step 5: Click on the green right mark, which is nothing but apply.
Step 6: GParted will confirm once again if you want to apply the changes. Go ahead and click ‘Apply’.
Format Complete
That’s it.
METHOD 2: From the Terminal
You can do the formatting from the terminal too. First, launch the terminal as root. To do that, simply type root in the Applications search box and click on ‘New Root Tab’. You will have to enter the root password.
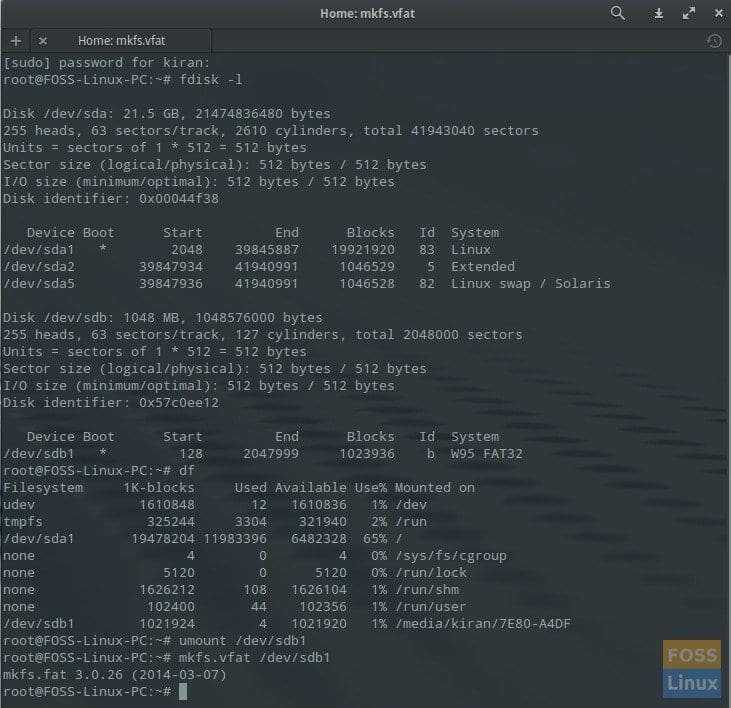
Terminal – Process of formatting USB Flash Drive
Enter the following command to see the list of all storage media connected to your PC.
fdisk -l
If you have a USB drive connected that you want to format, enter the following command to see a USB flash drive.
df
Typically, USB flash drives are mounted at /deb/sdb1.
Now umount the USB flash drive:
umount /dev/sdb1
Finally, enter the format command:
mkfs.vfat /dev/sdb1
The above command will format the drive to FAT32. If you want to format to NTFS, use the following instead:
mkfs.ntfs /dev/sdb1
That’s it.
Which method did you use? Would you please leave your comments below and share the article with your friends on social platforms? Remember the old saying, “Sharing is caring!”.


7 comments
Are you Kiran Kumar Chaudhary ?
In Gparted, the option to format in dropdown is disabled. Useless method.
Through terminal, fdisk -l fails to open as it displays permission denied.
Great!
Ubuntu 18.04 sucks
You have to unmount the drive you want to format before the format option is available.
Use sudo if permission is denied; sudo
Terminal method worked like a charm!
I have an external 1 TB HDD. Initially it had windows os and ubuntu 16.04 os in an acer machine that crashed. I have removed it and want to use it as an external HDD. I formated using windows and the data part was successful. The one with OS went to unallocated . i want to free it so that i have the whole 1TB for data storage. Ho do i attain that either in linux terminal or in windows?
Great post. I used to be checking constantly this weblog and I’m impressed!
Very helpful information specially the closing part ?? I deal with such info a
lot. I used to be seeking this particular information for a very lengthy time.
Thanks and best of luck