Sometimes resetting your Ubuntu network is required to apply some network configurations like changing your IP from Automatic DHCP to static one. Restarting it is not a big deal, but should be done carefully.
It is highly recommended not to perform such an action remotely using SSH because once you stop the network, your SSH connectivity will be lost. In some rare cases, you will not be able to start the connection through SSH. You will just need to be connected to the Ubuntu machine directly.
Restart Networking on Ubuntu
In this guide, we are going to show you how to restart your Ubuntu machine network using the following techniques:
- Graphical user interface or (GUI) tool
- Command-line or (Terminal) method
Now let’s start discussing each method separately.
Method 1: Restart the Ubuntu Network Using Graphical User Interface or (GUI)
In general, using any graphical tool is considered the easiest method to do whatever you need. In our tutorial, we shall use the NM-applet, which is a built-in applet for the Ubuntu network-manager, and it is found in the system tray. Below you can find detailed steps to restart the network connection using the NM-applet.
Stop Network
Step 1. First, let’s open the NM-applet; from the top panel, you can find a symbol for your network icon, which indicates that you are connected to the internet. Now click the down arrow.
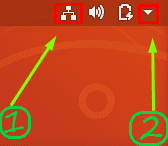
Click The Down Arrow
Step 2. Select the “Wired Connected” option.
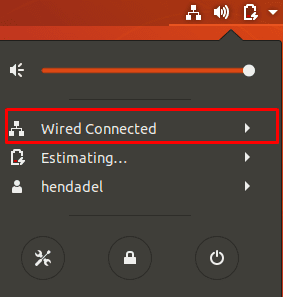
Click The Wired Connection Option
Step 3. Next, choose the “Turn Off” option to stop the network manager.
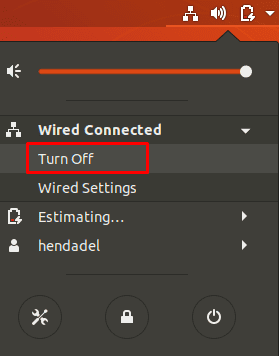
Click Turn Off Button
As you can notice, the network icon will disappear from the top panel, which indicates you are now offline.

Network Connection Is Down
Start Network
To start the network again, click the down arrow from the top panel. Then click the “Connect” option. You can now find the network icon appears in the top panel again.
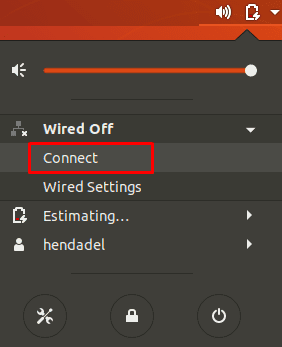
Press The Connect Button
Method 2: Restart the Ubuntu Network Using Command-Line
Besides the NM-applet graphical tool discussed in the above method, you can easily restart the network connection using command-lines. Some of those commands will make the network icon disappear from the top panel, and some will not affect its appearance. Hence, sometimes you may stop the network while the network icon still exists in the top panel, but meanwhile, you will be disconnected and will not be able to use the internet.
Restart Networking Service using init.d
Stop network service using the next init.d command. Make sure that you have sudo privileges to run these commands.
sudo /etc/init.d/networking stop or sudo service networking stop
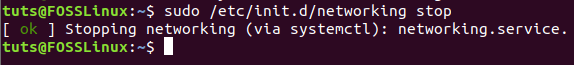
Stop Network Service
To start the network service again.
sudo /etc/init.d/networking start or sudo service networking start
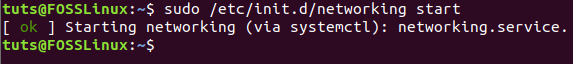
Start Network Service
The previous four commands can be used with Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and older versions. However, for newer Ubuntu versions you can use the below commands:
sudo systemctl restart networking.service
or the following command too:
sudo systemctl restart networking
Restart Network Manager Service
Using the below command will stop and start the network manager immediately, so the network icon may not disappear. To restart the network-manager service, use the following command:
sudo service network-manager restart
Restart Network Manager
Restart Network Using nmcli Command Tool
This command is widely used by Linux administrators to restart the network. Again you need to ensure you have sudo privileges.
sudo nmcli networking offStop Network Service Using nmcli
To start the network again using the following command:
sudo nmcli networking onStart Network Service Using nmcli
Restart Network Using ifdown/ifup Command
Additionally, you can restart the network interface immediately using the ifdown and ifup commands. To stop the network interface use the following command:
sudo ifdown -a
Stop Network Interface Using ifdown command
To start the network interface again, use the next command:
sudo ifup -a
Start Network Interface Using ifup Command
That’s it for now. I hope you have enjoyed this tutorial.

2 comments
So on a clean install of 20.04:
$ sudo systemctl restart networking
Failed to restart networking.service: Unit networking.service not found.
$ sudo systemctl restart networking.service
Failed to restart networking.service: Unit networking.service not found.
The correct command is sudo systemctl restart network-manager.service (.service may be omitted)
$ sudo service network-manager restart
on a headless Ubuntu 20.04, resolved my issues with Deluge not obtaining an IP address.
Also, I am using Windows 10 Remote Desktop Connection and did not have to reconnect.