Have you ever needed to view/edit a file or even open a directory that needs some administrative privileges? As a normal user, you will not be able to view or open or edit files and directories with administrative privileges. However, in Linux, you can perform any task that requires administrative rights using the sudo command.
Using the sudo command, you will be allowed to perform any administrative task. However, to use the sudo command, the user should be added to a sudo group. Using the sudo command, you will be able to run any other command as a high privileged user.
Adding Users to Sudoers
In this tutorial, we are going to cover how to create a new user and assign this user to the sudo group. Even more, we will show you how to remove a user from the sudo group and revoke the given administrative privileges from this user. This tutorial was executed on Ubuntu 18.04LTS. Now, let’s discuss the following points:
- Creating a new user
- Adding a user to the sudo group
- Removing a user from the sudo group
Creating a New User
In general, to create a new user in Linux, you should use the “adduser” command. So, the next command can be used to create a new user named “testuser”:
sudo adduser testuser
Add New Test User
To use the “adduser” command, you need to be a root user, or you can use the sudo command to create a new user. Now, you will be asked to enter the new user password.
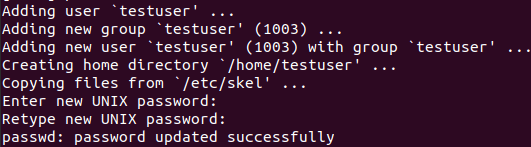
Enter Password For New User
Moreover, you need to add some additional information, or just you can leave them blank.
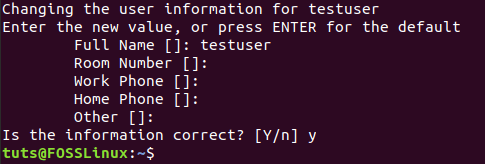
Enter Additional Information
The “testuser” is created successfully.
Adding a User To The Sudo Group
After creating the new user, you can now add this user to the sudo group using the next command:
sudo usermod -a -G sudo testuser

Add User To Sudo Group
To make sure that the newly created user was added to the sudo group, you can use the following command:
sudo -l -U testuser
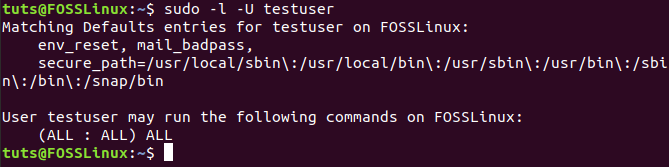
New User Added To Sudo Group
As you can notice, the output of the previous command will tell you the new user was added successfully to the sudo group. Now you can log in to the newly created user and start using the sudo command.
su - testuser
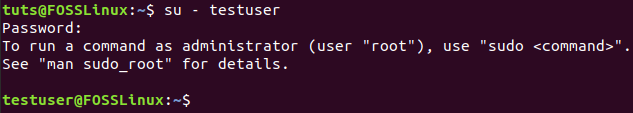
Login Using Newly Created User
As you can notice, you will get a message telling that to run a command as an administrator, and you can use the sudo command. Now, let’s create a new directory using the sudo command.
sudo mkdir newdir
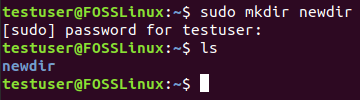
Create New Directory Using Sudo
Congratulations, you are now in the sudo group and can execute any command as an administrator.
Removing a User From The Sudo Group
What if you need to delete the granted administrative privilege from a user? Do not worry this easy you will just need to logout from the new user as follows:
exit

Logout
Next, use the “deluser” command to remove the user from the sudo group as follows:
sudo deluser testuser sudo
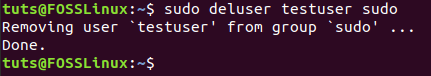
Remove New User From Sudo Group
As you can see in the previous screenshot, the new user was removed from the sudo group. Moreover, you can make sure that the user is not in the sudo group using the next command:
sudo -l -U testuser
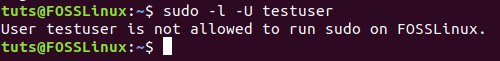
Newly Created User Is not Allowed To Use Sudo Command
As you can see in the above screenshot, the user is not allowed to run a sudo command because the user was removed from the sudo group. So, let’s login and try to use the sudo command.
su - testuser
Login To New User Again
sudo mkdir newdir

Use Sudo Command Again
As you can notice, the logged-in user is not in the sudo group, and hence the user will not be able to use the sudo command anymore.
Finally, you have now learned a new command that can help you a lot using Linux. That’s it for now, and I hope you have enjoyed this quick tutorial.

