The FreeBSD Release Engineering Team has announced the release and availability of FreeBSD 12.2 to the masses. It is the third and final release of the stable/12 branch. This post will cover the features and changes you can expect with FreeBSD 12.2 release. We will also give you a step-by-step guide on how to upgrade from your current version to FreeBSD 12.2.
FreeBSD 12.2 Features
FreeBSD by default doesn’t come packaged with a Desktop Environment like most of the Linux distributions. However, that doesn’t mean you can’t install one. Therefore, most of the features and updates are focused on the general system performance and not the user interface. Let’s dive in!
1. Userland Configuration Changes
FreeBSD 12.2 comes with a new rc.conf variable – the linux_mounts_enable. This new variable is used when specific Linux filesystems are mounted in the /compat/linux directory and the linux_enable variable is set to YES.
rc.conf is a configuration file containing configuration details of various network interfaces in the system, the local hostname, and information about startup services initialized at boot time. The rc.conf is utilized by various startup scripts found in the /etc., directory to conditionalize their execution with the settings in this file.
The linux_enable is a boolean variable when set to YES enables Linux/ELF at boot time.
Additionally, the devd the utility is updated to change the default syslogd notification for resume from kern to kernel.
The devd is a daemon that provides a platform for the execution of userland programs triggered by various kernel events.
2. Userland Application Changes
The cron utility is updated to support two new flags in crontab – ‘-n‘ and ‘-q.’
The -n argument suppresses mail on successful runs while the -q argument suppresses the logging of command execution.
- The
ddcommand is updated to support several additional arguments:- conv=fsync
- conf=fdatasync
- oflag=fsync
- oflag=sync
- iflag=fullblock
- The
fsck_msdosfsis updated to support some additional features.
They include reducing the memory footprint, a new argument, -M which disables the use of mmap utility, and others. fsck_msdosfs is a utility used to check the Windows (FAT) filesystem consistency.
- Support for
certctlutility.
certctl is a command-line tool used in managing a list of TLS Certificate Authorities that are trusted by applications that use OpenSSL.
showmountutility is updated to support long options.
showmount is a Linux utility used to get the status of the NFS server located on the host.
- The
sedutility is updated to read commands from stdin when the “-f” argument is specified. - The
bhyveutility is updated to support setting additional AHCI controller parameters. - The
jailutility is updated to allow running Linux® in a jailed environment.
3. Contributed Software
Software | Updated To ... |
|---|---|
| tcsh utility | version 6.21.00 |
| less utility | version v551 |
| libbsdxml library | version 2.2.9 |
| resolvconf utility | version 3.9.2 |
| pcap library | version 1.9.1 |
| tcpdump utility | version 4.9.3 |
| xz utility | version 5.2.5 |
| OpenSSH | version 7.9p1 |
| Timezone database files | version 2020a |
| unbound utility | version 1.10.1 |
| libarchive library | version 3.4.3 |
| private apr library | version 1.7.0 |
| svn{,lite} utility | version 1.14.0 LTS |
| ntpd suite of utilities | version 4.2.8p15 |
| file utility | version 5.39 |
| bc utility | version 3.1.1 |
| private sqlite3 utility | version 3.32.3 |
| BSD make utility | version 20200719 |
| Sendmail utility | version 8.16.1 |
| clang, llvm, lld, lldb, compiler-rt utilities and libc++ | version 10.0.1 |
| OpenSSL | version 1.1.1h |
FreeBSD 12.2 also comes with several software updates to enhance the general functionality of different software. For example:
- The
nctool has received an update to include a new--sctpargument. - The
mtreeutility also received an update to handle issues like the-fargument not considering type changes, and more.
4. Deprecated Software
Other than updates, there is also software marked as deprecated. The amd utility is one and is targeted for removal in FreeBSD 13.0 release.
5. Runtime Libraries and API
With FreeBSD 12.2, the ifconfig utility has received an update and can now report a bridge interface status.
6. General Kernel Changes
readsystem call will now disableread()call by default on folders and directories.- FreeBSD 12.2 comes with the
ixldriver enabled by default. - The
machdep.kdb_on_nmivariable on sysctl is removed. Additionally,machdep.panic_on_nmivariable will now directly enter the debugger. The sysctl is a utility responsible for retrieving the Kernel state. - FreeBSD 12.2 also includes support for APEI (ACPI Platform Error Interfaces)
7. Devices and Drivers Changes
With this new release, several drivers are marked as deprecated and removed in FreeBSD 13.0 release and later. They include:
ubsec– Enables support for Broadcom and BlueSteel cards that contain the uBsec 5x0x crypto accelerator chips.ufm– Enables support for D-Link/GEMTEK FM tuner.apm– Enables support for Alliance ProMotion video cards.ctaucx
8. Storage Changes
The mps driver, which enables support SAS controllers and WarpDrive solid-state storage cards for Broadcom is removed from the 32-bit GENERIC kernel configuration.
The virtio_blk driver, which enables support for VirtIO block devices, has received an update to include TRIM support.
Additionally, the ZFS filesystem now supports read/write kstat output per dataset.
9. Boot Loader Changes
With FreeBSD 12.2 release, users will now access the konsole from the bootloader and can select any of the available console devices.
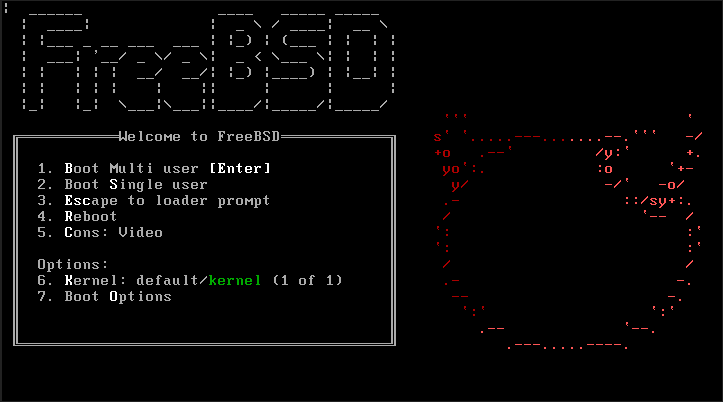
FreeBSD console
10. General Networking changes
FreeBSD tends to have a large market on servers than Desktops. Therefore, users can expect quite some updates in the networking part of the entire operating system. Below are some of the updates and changes.
- The
tabandtundevices will now create/devaliases whenever they are renamed. - The
ipfwdriver now includes support for RFC6598/Carrier Grade NAT subnets. - The
ng_natwill now support to attach an ethernet interface.
The drivers updated to a new version include:
ixlis updated to version 1.11.29enais updated to version 2.2.0cxgbeis updated to version 1.25.0.0
Additionally, a set of new drivers have been added to this new release to enhance support for 802.11n and 802.11ac. FreeBSD 12.2 will also include support for Intel 100GB Ethernet cards with the new ice driver.
Upgrading to FreeBSD 12.2
Now that you have seen some of the cool features FreeBSD 12.2 brings forth, you are probably thinking of upgrading your current system. Don’t worry, that’s what we will cover in this system.
- Download and install the freebsd-update utility. Execute the commands below:
freebsd-update fetch freebsd-update install
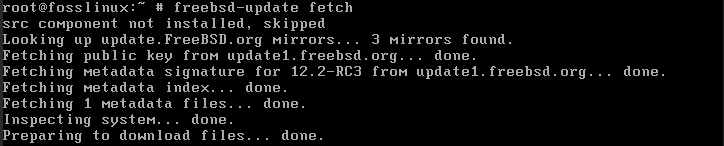
update fetch
- Now, you can use the freebsd-update utility to fetch and install the updates.
freebsd-update upgrade -r 12.2-RELEASE freebsd-update install
- After a successful installation, reboot the system with the command below:
shutdown -r now
- Once the system reboots, execute the freebsd-update install command again to install the new userland components.
freebsd-update install
That’s it! You have updated your system to the latest FreeBSD 12.2 release. You can go ahead to execute the uname -a command to see the FreeBSD version you are currently running.
uname -a
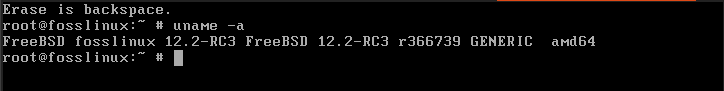
uname command
Conclusion
This post has given you a clear insight into some of the features that come with the FreeBSD 12.2 release and the whole upgrade process. Since this operating system doesn’t come with a pre-installed GUI, most of the updates and changes aim to improve the general system performance. If you are not ready with upgrading your system to this latest release, you can install it as a virtual machine and test its performance before using it for production.