If you want to be a master of ethical hacking and grasp the understanding of possible loopholes or vulnerabilities of a system or systems existing under a defined network, then you have no choice but to turn to Kali Linux. It documents, versions, and parades the best tools in the Cybersecurity industry to use for penetration testing. The extensive documentation and community support of these penetration tools make a beginner’s first step into the Cybersecurity world a stressless joy.
If we journeyed back 20 years ago and previewed the calendar state of Cybersecurity, you would not be able to fit in this world as easily as you can now. Nothing was straightforward, and the available penetration tools were not exposed to thorough documentation. Such a gamble would require a standardized technical endurance level, which would make normal learning a dull adventure.
Kali’s penetration tools ensure that you know and understand the vulnerability workaround of your web apps and systems. You can put to the test the security infrastructure strength of a target system. You will gauge the chances of a system or web applications against real-life attacks from network loopholes. The penetration testing metric in use defines various workable tests that you must simulate to determine the system’s security strengths and weaknesses or web app under study.
Why Kali Linux for Penetration Testing?
The primary reason why Kali Linux is considered the ideal OS for penetration testing is its free and open-source attribute of this Debian-defined Linux distro. Moreover, the developers behind its creation are housed by Offensive Security. It is a renowned and highly valued security system entity that empowered Kali Linux to be sort after by security experts and companies.
Offensive Security also has a hand in the initiation of various ethical hacking courses that make experts out of beginner Linux users. You do not need to walk this road alone to be a renowned and recognized system penetration tester. Offensive Security is responsible for Kali Linux’s reputation and why we use it.
Top 25 Kali Linux Tools
The 25 Kali Linux penetration tools that have caught the eye and attention of this article were fished out based on a unique criterion. We considered the penetration tool’s functionality and implementation procedure or Penetration Testing cycle. The penetration tools we will be previewing are just needles in a haystack of 600 other Kali Linux ethical hacking and penetration tools. Before we dive into these exciting tools, it is paramount that a potential penetration tester first familiarizes themselves with the Penetration Testing Cycle.
The Penetration Testing Cycle
The first knowledge base of a potential ethical hacker is understanding the functional and design architecture of any system or app under study. An instance like a Wireless Network understudy requires a student of penetration testing to know things like the active Internet Service Provider (ISP), present active routers, clients like remote computers, CCTV, users, etc., to mention a few.
An internet’s workaround as a network depicts it as a large and complex system. A Penetration Testing Cycle relates to the procedures a user must follow to successfully penetrate or exploit a targeted system or web app through its hostname or IP address. A Penetration testing Cycle exists in three states.
Step 1. Reconnaissance
This step should be obvious as it needs the penetration tester to gather all the needed information about the targeted system or web app. A popular tool for reconnaissance is the traceroute utility. It will trace the road map of the site you want to study. You can install it and try it on your terminal.
sudo apt install inetutils-traceroute sudo apt install traceroute traceroute fosslinux.com
My results are as follows.
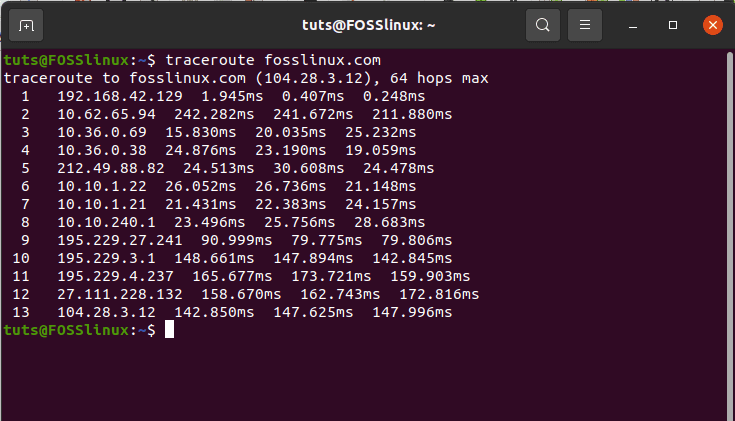
Reconnaissance with the traceroute utility
Step 2. Scanning
The Reconnaissance step traced the sequential routes followed by data packets within the FossLinux domain, and the 13 hops from the screenshot are evident enough. The listed IP address hops also include my current Internet Service Provider. This list can also include the router gateway. This scanning step explores the active services defining the exposed IP addresses. A renowned tool for network scanning, which we shall also list under this article, is Nmap. If you were to expose the services of an IP address after traceroute, you would need to adhere to the following Nmap syntax rule.
Nmap -v -sS [Your Desired IP Target] -Pn
The command arguments -v is for enabling verbose mode, -sS for implementing the TCP SYN scan technique, and -Pn skips host discovery and assumes the targeted host is online. Do not worry about the technical explanations behind these arguments, as they will make more sense once you take a practical approach towards learning and exploiting them.
Step 3. Exploitation
The final step is exploitation. Since you have the desired IP address and the services catering to it, you are in a position to initiate real network or system penetration testing. An instance we can relate to would be using a utility like Nmap that exposes an IP address’s vulnerability through an SSH server if the target web app has an open port. This outcome implies that the system or network is vulnerable to an easy brute-force attack or dictionary attack. Kali Linux has powerful tools like Hydra, which can successfully achieve network penetration on such a vulnerable hostname. Knowing a penetration tester is important as it helps you expose and fix the loopholes on a network or system under study.
We might have slightly deviated from the objective of our article, but it was worth it. You now have an idea of where to begin before you start launching the canine teeth of the Top 25 Kali Linux penetration testing tools. Let us now categorically list them based on the functionalities or features they offer.
POST EXPLOITATION
1. Metasploit Framework
Metasploit Framework
It is one of the top-rated tools under Kali Linux due to the numerous prepackaged modules it brings to the table. An exploit can be defined as a vulnerability on a system, application, or service identified by an attacker. An exploit has four main attributes: payload, Auxiliary, Encoders, and Post. A payload is a code snippet that executes after successfully exploiting a targeted system. This running code can be used to steal user-privileged data and compromise the system’s integrity.
An auxiliary initiates additional functionalities like a DOS (Denial of Service) attack to an initiated exploit. It does not implement a payload. Encoders hide an attacker from configured system firewalls or anti-viruses. It is successful by initiating an encoded backdoor, which the target system user unknowingly grants authoritative access. Post caters for post-exploitation of a compromised system by empowering the attacker to dig deeper into the exposed system through availed Metasploit Framework modules. Metasploit exists in several interfaces: CobaltStrike, Web Interface, Armitage, msfgui, msfcli, and msfconsole.
SNIFFING AND SPOOFING
2. Wireshark

Wireshark
To successfully sniff and spoof a target system or app on a network, you need a network analyzer tool. Wireshark is such a tool and employs its effectiveness in network security auditing. Its use of display filters generalizes packet filtering where an attacker or network auditor can capture exposed passwords. For instance, a filter like addr==10.20.2.2 will target the set IP address. Also, a filter like port eq 30 or icmp will display results related to the specified port 30 and also the ICMP traffic. Finally, a filter like request.method==”POST” might expose a user password on the network. Initiating Wireshark will prompt you to configure your desired network interface through its Graphical User Interface.
3. Bettercap
Bettercap
The power and portability of this utility make it ideal for network-based MITM attacks, real-time TCP, HTTP, and HTTPS traffic manipulation, and many other network attacks like sniff for credentials. It works against HSTS preloaded, HSTS, and SSL/TLS by bypassing them through its use of SSLstrip+ and dns2proxy (DNS server). The real-world application of the latter statement leads to the termination of an SSL/TLS connection. The SSL/TLS connection linking the attacker and the target client is decrypted.
Such a bypass on an SSL/TLS connection will trick and redirect a client visiting a specific web-hosted domain name to a fake domain via HTTP redirection. If a user is not paying attention to the URL bar, they might find themselves on a domain name interface with an extra w in web or www. Such a URL definition excludes a web host from the HSTS preloaded hosts membership list. A special DNS server completes this attack by resolving the fake domain names with real IP addresses. A sniff and spoof attack then occurs from the new domain name environment where a user can enter credit information or passwords captured by the attacker.
EXPLOITATION
4. Social Engineering Toolkit (SET)
Social Engineering Toolkit
Information security defines social engineering as the psychological manipulation of users existing in a defined network into exposing or revealing their confidential information. SET, an open-source penetration framework, implements various custom attack vectors in its execution. They include mass-mail, spear-phishing, phishing, and malicious USB. Trustedsec is responsible for the existence of this free toolkit product.
WIRELESS ATTACK
5. Fluxion
Fluxion
It is an Evil Twin wireless attack tool you should consider prioritizing. It does not take the brute-force approach to break a network key but rather targets a Wi-Fi network through its created open twin AP. An instance where a user needs to connect to a set Wi-Fi network leads to the popup of a fake authentication network page. This user then unknowingly enters a valid network key, which Fluxion captures. It will match the captured network key by comparing it to a network handshake to ensure its validity. Fluxion functions perfectly because of its dependencies. It installs automatically. It also provides Fluxion wizard instructions for assistance.
6. Aircrack-NG Suite
Aircrack-NG Suite
This wireless attack toolkit exists as a network software suite. It consists of a packet sniffer and a scanner. An important item that completes this list is the WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK cracker and analysis toolkit. This tool caters to 802.11 wireless LANs. Numerous essential modules exist under Aircrack-NG Suite. They include airtun-ng for creating a virtual tunnel interface, ivstools for merging and converting purposes, tkiptun-ng for WPA/TKIP attacks, and airserv-ng, which permits remote access to wireless cards. These modules are just a drop in the ocean of many others available and rich in functional performance.
PASSWORD ATTACKS
7. THC Hydra
THC Hydra
It is a popularized Online Password Cracking Service. This password attack tool is rated as one of the fastest in the Cybersecurity domain. Its support for many attack protocols makes it a reputable network login cracker. A few of its renowned and supported protocols include XMPP, Cisco AAA, VNC, Cisco Auth, VMware-auth, Cisco-auth, Telnet, CVS, Teamspeak(TS2), FTP, Subversion, SSHKEY, SOCKS5, SMTP Enum, SMTP, SIP, Rlogin, RDP, PostgreSQL, ORACLE SID, ORACLE Listener, HTTP(S)-HEAD, and HTTP(S)-FORM-GET.
8. John the Ripper
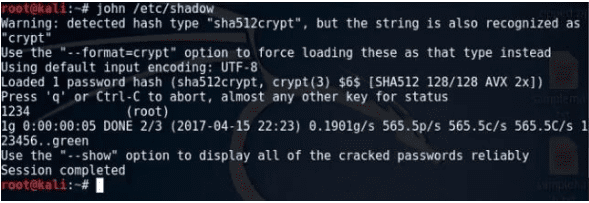
John the Ripper
It is a renowned Offline Password Cracking Service. John the Ripper is a popularized Kali Linux tool because of its effectiveness in cracking programs and testing passwords. Its functional algorithm can be broken down into three steps. First, it prepackages and combines the functionality of several password crackers at once. Secondly, it will auto-detect a targeted password’s hash. Finally, it integrates a customized password cracker to complete the attack. For example, a Linux system will have the system’s user password on the file path /etc/password. The accompanying SHA encryption for these user passwords is on the file path /etc/shadow. An incorrectly configured system will have John the Ripper expose the vulnerabilities of such user-sensitive information.
9. Crunch
Crunch
We can define Crunch as a Kali Linux tool that has mastered the art of generating combinations and permutations based on existing custom wordlists with specified character sets or standard character sets. To understand the functional depth of Crunch, we have to look at the syntax behind its usage.
crunch <min> max<max> <characterset> -t <pattern> -o <output filename>
The arguments min and max define the maximum and minimum usable password lengths. The character set argument generates the needed passwords. We use -t <pattern> to specify the generated passwords’ possible patterns through combinations and permutations of details like the system user’s birth date, pet name, or favorite color. Finally, -o <pattern> will finalize the password attack by saving the generated wordlists to a specified file name and location. These wordlists are effective in attempting a network system breach.
10. Hash-Identifier and FindMyHash
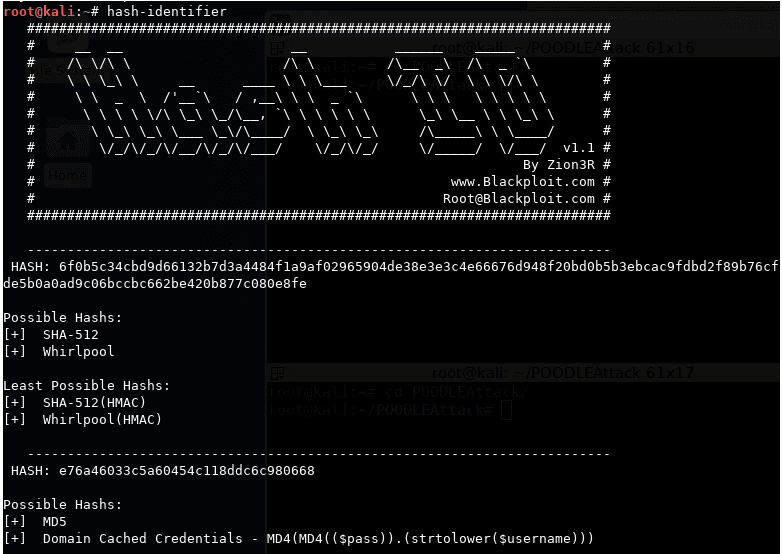
Hash-Identifier
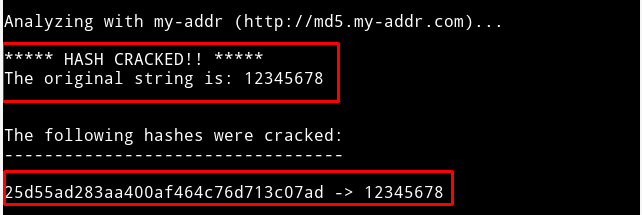
FindMyHash
A weakly encrypted user password or data will fall victim to a Hash-identifier password attack since the Hash-Identifier tool identifies and exposes the various hashes linked to them. On the other hand, Findmyhash will employ online services to crack encrypted user data and passwords successfully. The Hash-Identifier tool usage first requires the penetration tester or attacker to identify the relevant user password or data hash type. It will decrypt the provided data or password and identify the hashing algorithm used. Next, the Findmyhash tool will crack the provided user data or password.
DATABASE ASSESSMENT
11. SQLMap
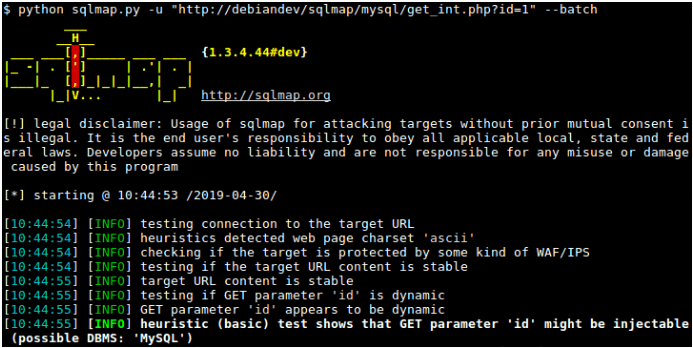
SQLMap
If you want to detect and exploit relevant SQL injection vulnerabilities on a targeted database system, you can swiftly automate this process through the SQLMap tool. The first step towards cherishing the importance of SQLMap is finding a target website URL that displays symptoms of SQL injection vulnerabilities. This initial step should not trouble you as you can find such vulnerable websites through Google dork and SQLiv. All you need is the vulnerable URL, and SQLMap will handle the rest through its terminal commands. The commands of this Kali Linux tools enable a penetration tester or user to acquire databases list, tables list, columns list, and the targeted database data. Such an attack or penetration test might require other Kali Linux tools when the targeted data turns out to be encrypted.
WEB APPLICATION ANALYSIS
12. JoomScan & WPScan
JoomScan
WPScan
The JoomScan tool targets the scanning and analysis of the Joomla CMS web application. In contrast, the WPScan tool will scan and analyze any vulnerability on a WordPress CMS web application. It is easy to identify the CMS type of a targeted website through tools like CMSMap and the ONLINE CMS Scanner. The analysis results of the targeted CMS websites will then determine if a penetration tester should use JoomScan or WPScan.
13. HTTRACK
HTTRACK
This tool is effective in cloning a web page or a website concerning the perspective of a penetration testing result. It primarily caters to creating fake website clones or server attacks through phishing. Launching this tool from the Kali Linux terminal provides a guided configuration set up requiring info like proxy configuration, the target website URL, and the project’s base path and name.
14. OWASP-ZAP
OWASP-ZAP
This tool will test a web app’s security through its Java-based platform. The availed GUI is intuitive and does not downgrade the effectiveness of its functional features like attacking, spidering, fuzzing, proxying, and scripting web apps. You can also extend its usage through compatible plugins. Hence we can define this web app testing tool as a complete package.
15. BurpSuite
Burpsuite
With this tool, web apps can put their security infrastructure’s status to the test. It will map and analyze the attack surface of the targeted web app through the discovery of potential security vulnerabilities and exploits. Its primary feature is its ability to function as a proxy interceptor, enabling it to hijack the traffic existing between a web server and a web browser.
16. SQLiv
SQLiv
This Kali tool determines the vulnerability of a web app through its SQL injection scanning functionality. You might not find the default installation on your Kali Linux distro, but you can install it through the following command.
git clone https://github.com/Hadesy2k/sqliv.git cd sqliv sudo python3 setup.py -i
The following command syntax should get you started with this penetration testing tool.
sqliv -t [Your Targeted URL]
VULNERABILITY ANALYSIS
17. Nikto
Nikto
This tool assesses both a web application and a web server and exposes the evident security vulnerabilities or other related issues. It will scan for a maximum of 6700 files and programs that are a risk to a system or network application. Its usage is straightforward and can be achieved from the following command syntax.
nikto -h [Target IP Address or Hostname]
INFORMATION GATHERING
18. Dirbuster / Dirb
Dirbuster
If a website is not good at hiding directories, files, or objects, Dirb will expose it. It employs and launches a dictionary-based attack against an active web server and, in return, performs an analysis of the web server’s response. A preconfigured wordlists’ set found at /usr/share/dirb/wordlists/ defines it. Its functional syntax is as follows.
dirb [Target] [Wordlists_file]
The argument Target is a website URL, and Wordlists_file is the path to the hidden directories, files, and objects.
19. NMAP
NMAP
Security auditors fancy the additional use of this Kali Linux tool, making it effective for network discovery. The –script option under a Nmap command will perform a complete audit of an open port’s security vulnerability.
nmap [Website URL] --script vuln
20. Maltegoce (Maltego Community Edition)
Maltegoce (Community Edition)
This Kali tool is categorized as an intelligence-gathering tool to discover and collect target data, which can be company-based or personal. Additionally, the collected data is visualized to initiate a graph-based analysis. Before using Maltegoce, you first need to be a registered member of the Maltego community as its launch screen will require those login credentials. Afterward, you will specify a target machine and then key in the related domain name for Maltegoce to perform its magic.
21. Whois

Whois
Local internet registrars are responsible for the management of this database tool. We can also look at it as a protocol-based query and response system that helps identify the users with full or partial ownership to listed internet resources. It links a domain name to a domain owner, and if such information is under the control of a vulnerable user, it can be a gateway to social engineering attacks.
22. WhatWeb
WhatWeb
It is a fingerprint utility for websites. It identifies embedded devices, CMS, web servers, blogging platforms, JavaScript libraries, and analytic packages. With over 1700 plugins, this tool can never miss the mark. It will expose SQL errors, web framework modules, version numbers, account IDs, and email addresses.
23. TraceRoute
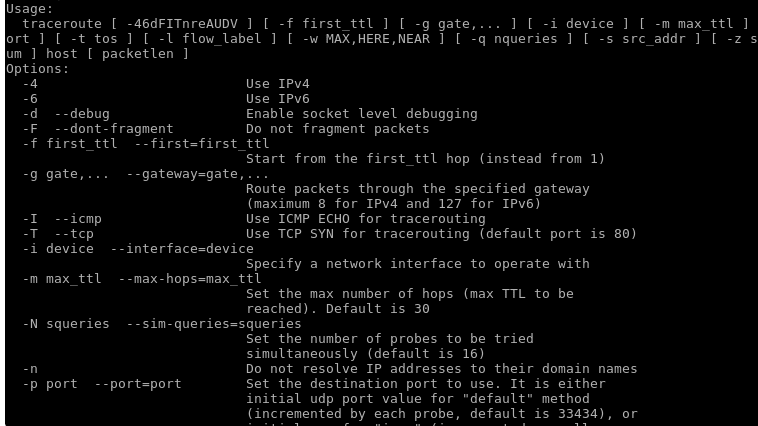
TraceRoute
If you are suspicious of an IP network’s tendency to delay its transmission of packets rate, a traceroute will expose this network’s connection route and also analytically measure the delay status of the data packets on transit. It also exposes the hardware gateways in play and their status.
ANONYMITY
24. ProxyChains
ProxyChains
This tool will cover and take care of any network job you assign it. All you have to do is prefix your target command with the keyword proxychains. A practical instance is triggering it to cover the Nmap command so that you can anonymously execute it. The command syntax for such a use-case is as follows.
proxychains nmap [Target IP Address] -v -T4
25. MacChanger
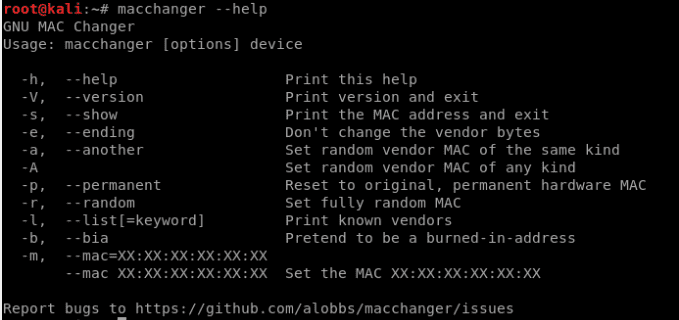
MacChanger
The importance of changing your MAC address regularly is one of the reasons why this tool exists. It keeps you from being predictably discoverable under an active network. You can use it to change a wireless adapter’s MAC address as much as possible.
macchanger -r [wireless device e.g wlan1]
Final Note
When it comes to perfecting your Cybersecurity skills through penetration testing, there is only one Linux distro that can swiftly help you accomplish this objective. Its name is Kali Linux. Moreover, there are several security certifications offered based on Kali Linux. This Linux distro is perfect for kick-starting your Cybersecurity career or fully exploiting it as a hobby.