Fedora 36 Beta is out to the masses. It ships with tonnes of unique features, and three of the most notable are:
- It uses the newly released GNOME 42, with some pretty exciting UI updates and features. You can check out our post -‘ What’s new in GNOME 42.’
- It ships with Linux kernel 5.17
- The RPM databases will now be stored in /usr instead of /var subvolume. That will make the whole process of managing system snapshots much more effortless.
You can view all the features and updates you can expect on this new release in our post – ‘What’s new in Fedora 36.‘
Upgrading to Fedora 36 Beta
This post will guide you through upgrading from Fedora 35 to Fedora 36 Beta. Note that we are upgrading Fedora to a beta version. We don’t recommend doing it on a production machine until the final Fedora 36 is out.
We will use two main methods:
- Update to Fedora 36 via Command-Line
- Update to Fedora 36 via the Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Tip: Please ensure you have an active internet connection.
Method 1: Update to Fedora 36 Beta via command-line
If you are a terminal person, this is the method for you. However, if you are also not well-versed with the Terminal commands, don’t panic! Just copy-paste the commands and execute them on your system, as shown in the screenshots.
First, check your current Fedora version using the command below.
cat /etc/fedora-release
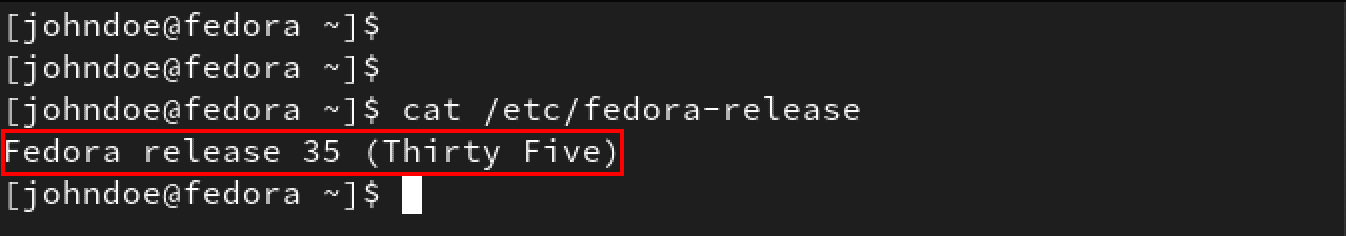
Fedora version
Ensure you are running Fedora 35. If you are still running an earlier version of Fedora, like Fedora 34, you will need to first upgrade to Fedora 35. Check out our post – ‘How to upgrade from Fedora 34 to Fedora 35.’
When done, follow the steps below to get started.
Step 1. Update the system and remove obsolete packages
To avoid any errors during the upgrade, ensure your system is running up-to-date packages by executing the command below on your system.
sudo dnf upgrade --refresh
Note: This process might take quite some time (up to 30 minutes) if you have not updated your system for a long time. It is also dependent on your internet connection speed.
Upgrade system
Next, you need to remove all outdated packages since they might bring conflict errors. Execute the command below.
sudo dnf autoremove
Remove obsolete packages
Step 2. Configure DNF speed and mirrors
Upgrading from one Fedora release to another can take quite some time as you will need to download a big pack of packages. We can try to optimize this process by increasing the DNF speed and using the fastest repository mirrors.
To get started, install DNF plugins using the command below.
sudo dnf install dnf-plugins-core
Upgrade tool
Next, open the DNF configuration file using the nano editor. Use the command below.
sudo nano /etc/dnf/dnf.conf
The first trick to increase the DNF download speed is enabling parallel downloads. By default, DNF downloads a single package at a time, and we can set it to download 10, 15, or 20 packages simultaneously. However, we recommend setting it to 10 and then trying the other options.
Add the line below at the end of the DNF configuration file.
max_parallel_downloads=10
DNF does not use the fastest mirror to download the packages by default. Luckily, you can force it to use the quickest mirror by adding the line below at the end of the configuration file.
fastestmirror=True
When done, your configuration file should look similar to the image below.
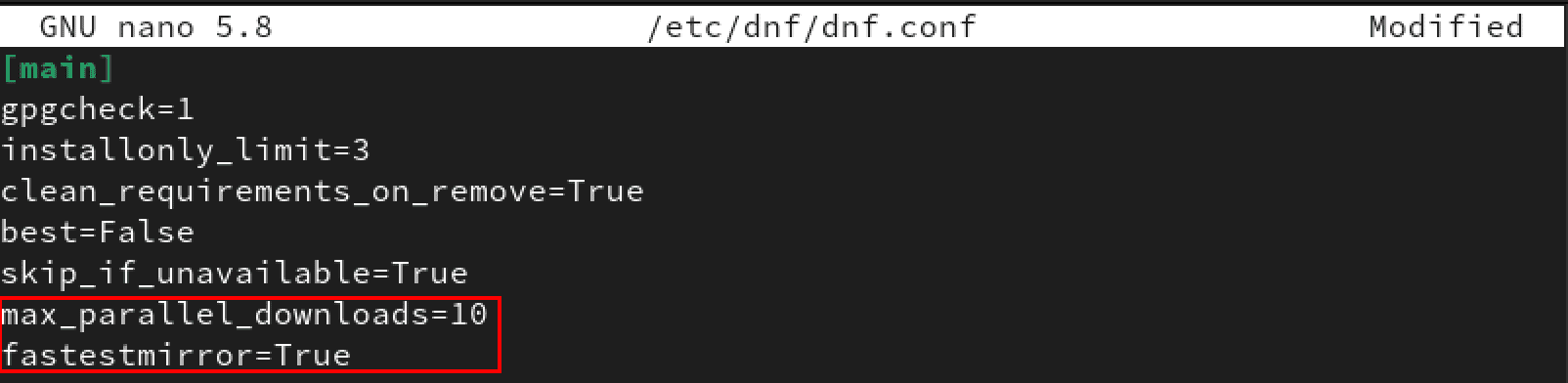
Configure DNF
Save the file (Ctrl + S) and Exit (Ctrl + X).
Step 3. Upgrade from Fedora 35 to Fedora 36 Beta
To upgrade from one Fedora release to another, we will use the dnf-plugin-system-upgrade utility. Even though it comes pre-installed in most Fedora releases, you can verify that by executing the command below.
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgrade -y
Now, to upgrade to Fedora 36, execute the command below.
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=36
You will see a prompt similar to the image below. If you have already run the dnf upgrade –refresh command, type ‘Y’ and press Enter to start the upgrade process.
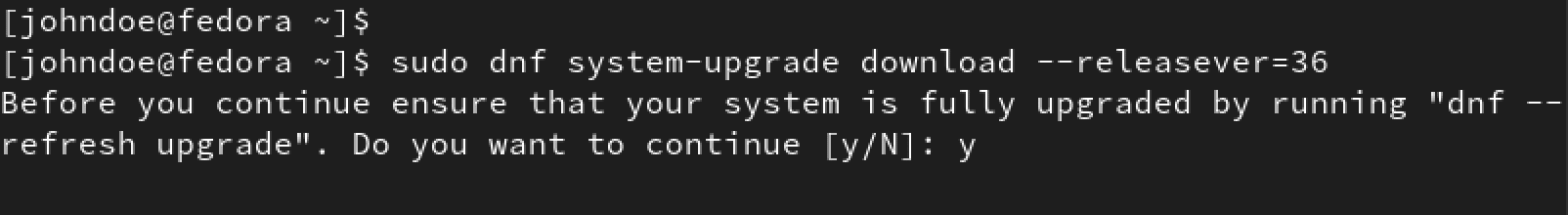
Upgrade to Fedora 36
Troubleshooting upgrade errors
If the command above prints any errors on the Terminal, try the solutions below in order.
- Add the
--allowerasingparameter in the upgrade command as shown below.
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=36 --allowerasing
The ‘–allowerasing’ parameter allows the system to delete any installed packages that are raising dependency errors
- If the ‘–allowerasing’ parameter doesn’t work, re-sync your system using the command below, then execute the upgrade command again.
sudo dnf distro-sync
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=36
After successfully running the system-upgrade command, you will see a prompt to perform the overall system upgrade. You will see a list of packages that will be downloaded, including the total download size. In our case, the system will download 1.7 GB of data. Type ‘Y’ to continue.
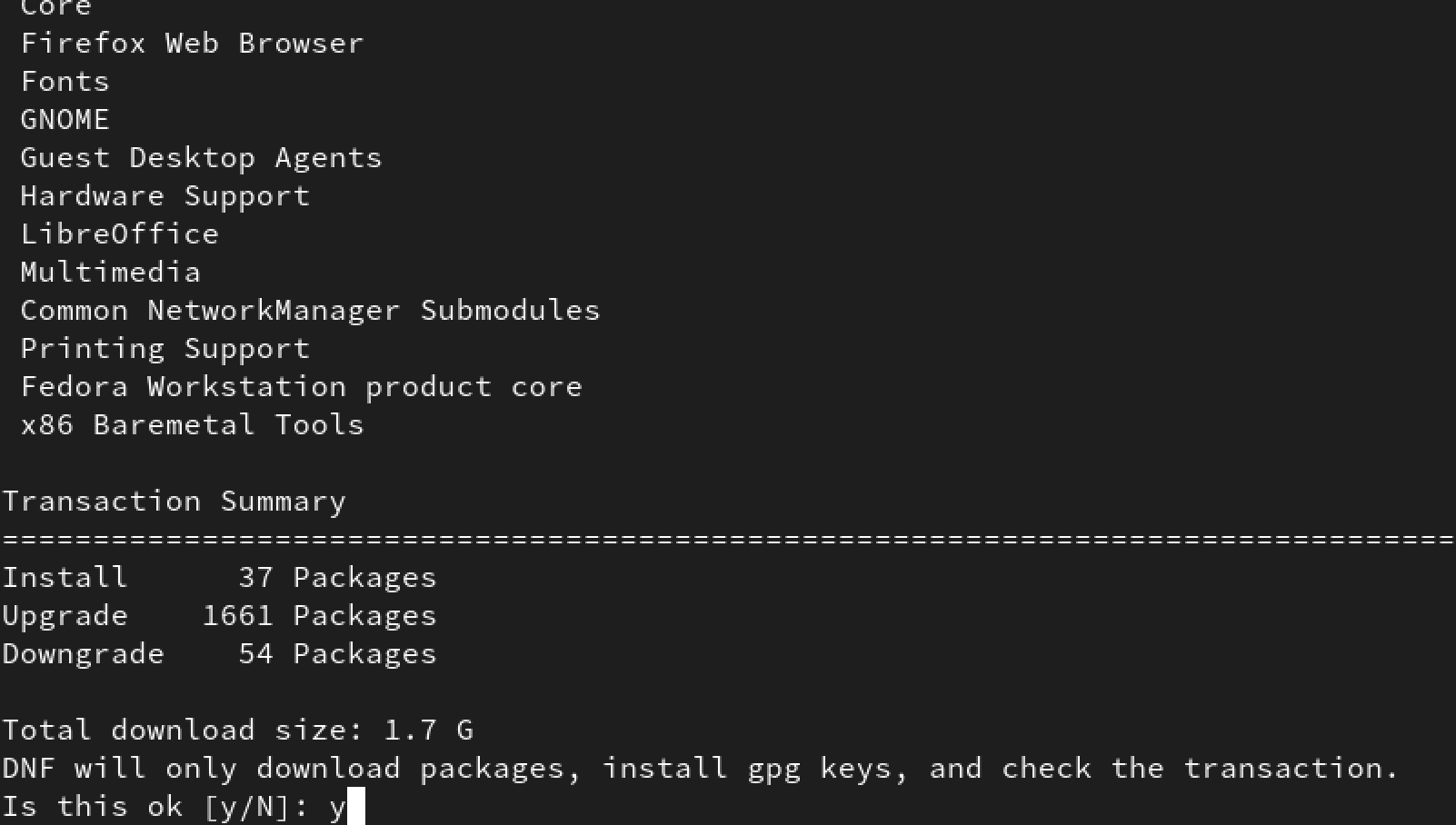
Upgrade Fedora
Depending on the download size and your internet speed, this process might take some time. Please be patient. You will see a prompt to import the Fedora 36 GPG key along the upgrade process. Type ‘Y’ and press ‘Enter.’
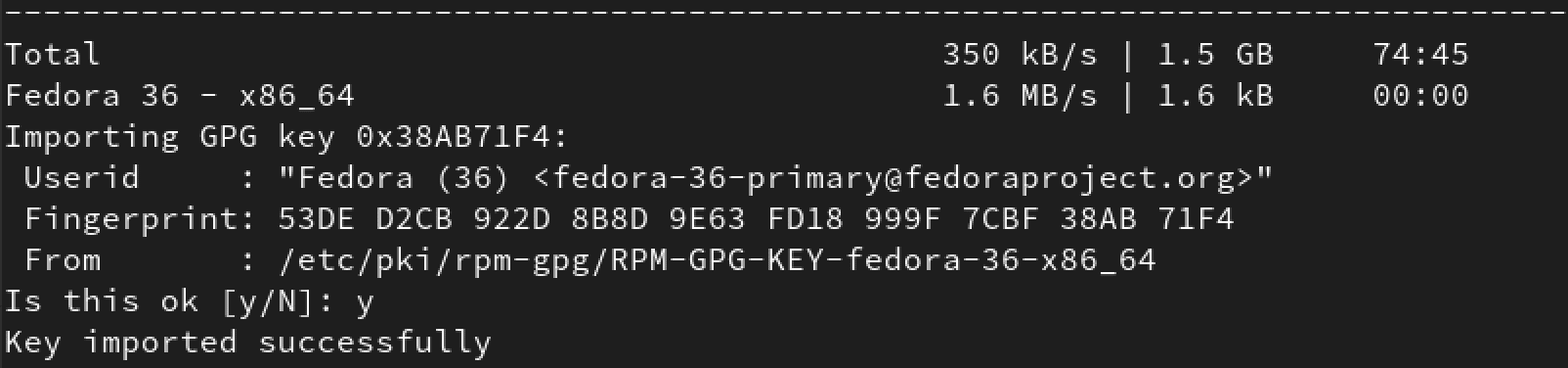
Import GPG key
A few minutes after successfully importing the GPG key, you will see a message that the download process is complete. You need to reboot your system. Execute the command below to restart your system and start the upgrade process.
sudo dnf system-upgrade reboot
You will see a graphical window with a progress bar showing the upgrade process.
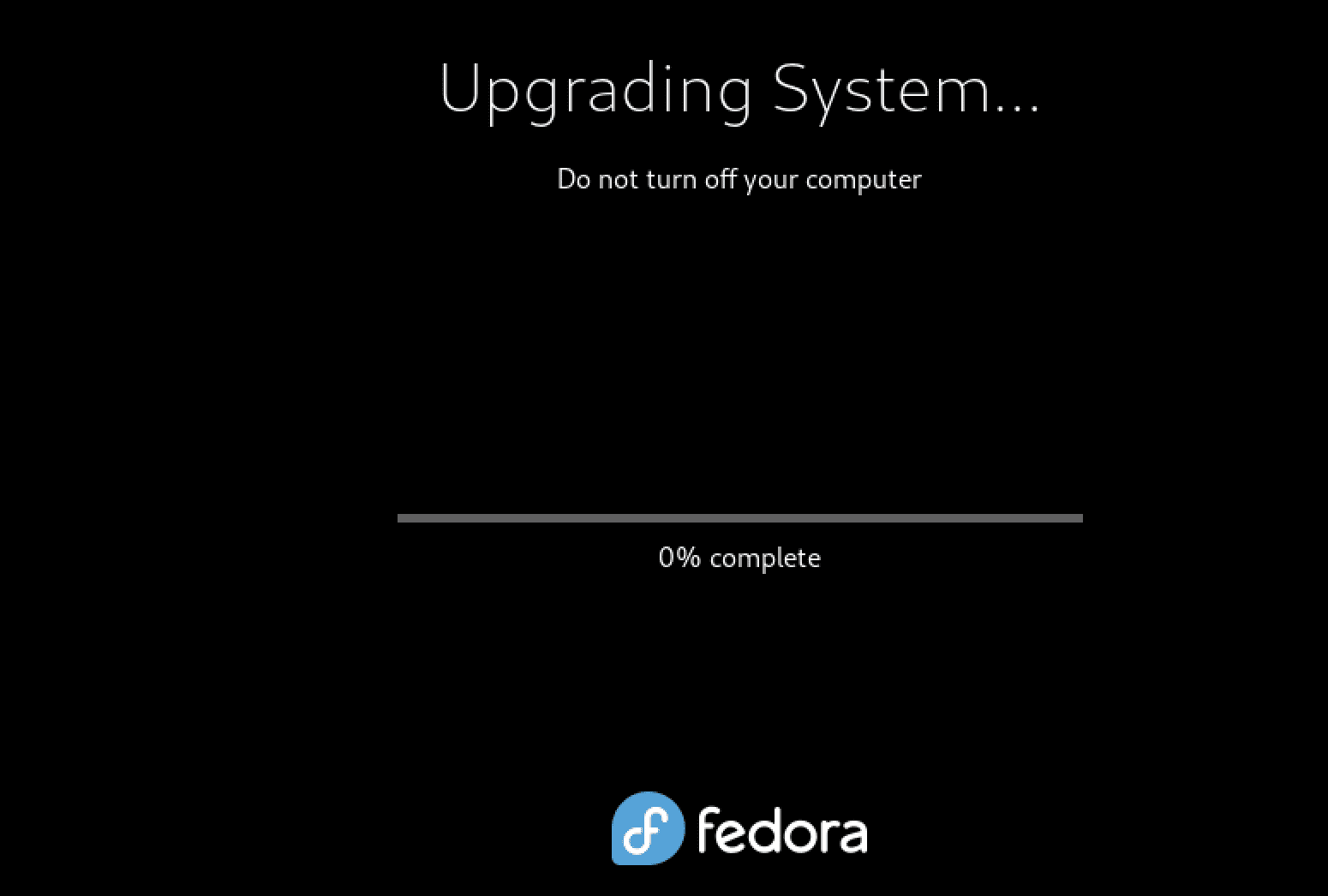
Upgrading System
After the upgrade process is complete, you will see the Fedora 36 login screen. Use your credentials to log in. The first thing you will notice is the beautiful Desktop interface with a new background image. You can verify whether you are running Fedora 36 by executing the command below.
cat /etc/os-release
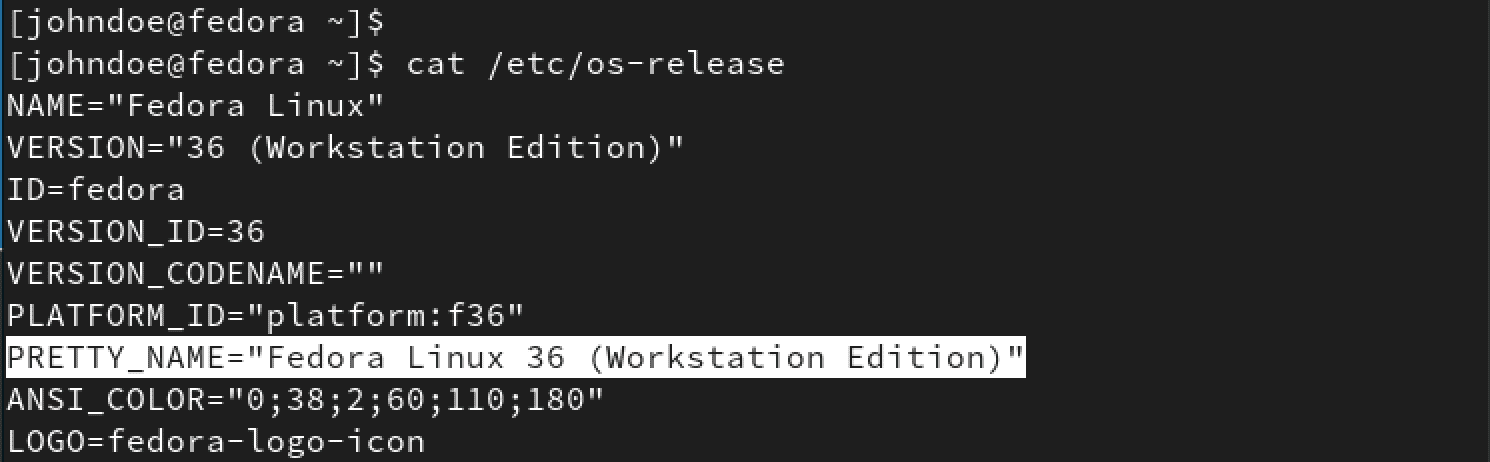
Fedora 36
Step 4. Post Upgrade Cleanup
if you are contented with the new Fedora release and don’t plan on reverting, it’s advisable to remove all the downloaded packages. Execute the command below.
sudo dnf system-upgrade clean
That’s it! You have successfully upgraded from Fedor 35 to Fedora 36.
Method 2. Update to Fedora 36 Beta with GNOME software center
If you are using the GNOME Desktop Environment, you can easily upgrade from Fedora 35 to Fedora 36 graphically using the GNOME Software Center. Or almost graphically. You will still need to execute one command on the Terminal.
gsettings set org.gnome.software show-upgrade-prerelease true
Launch the Software Center and select the ‘Updates’ tab when done. If you have any pending software updates, install them before proceeding with the OS upgrade. If you don’t see a banner showing you Fedora 36 release, you need to restart your system or kill the Software Center app with the command below.
pkill gnome-software
Re-launch the Software Center, and you should now see Fedora 36 available for download. Hit the ‘Download‘ button.
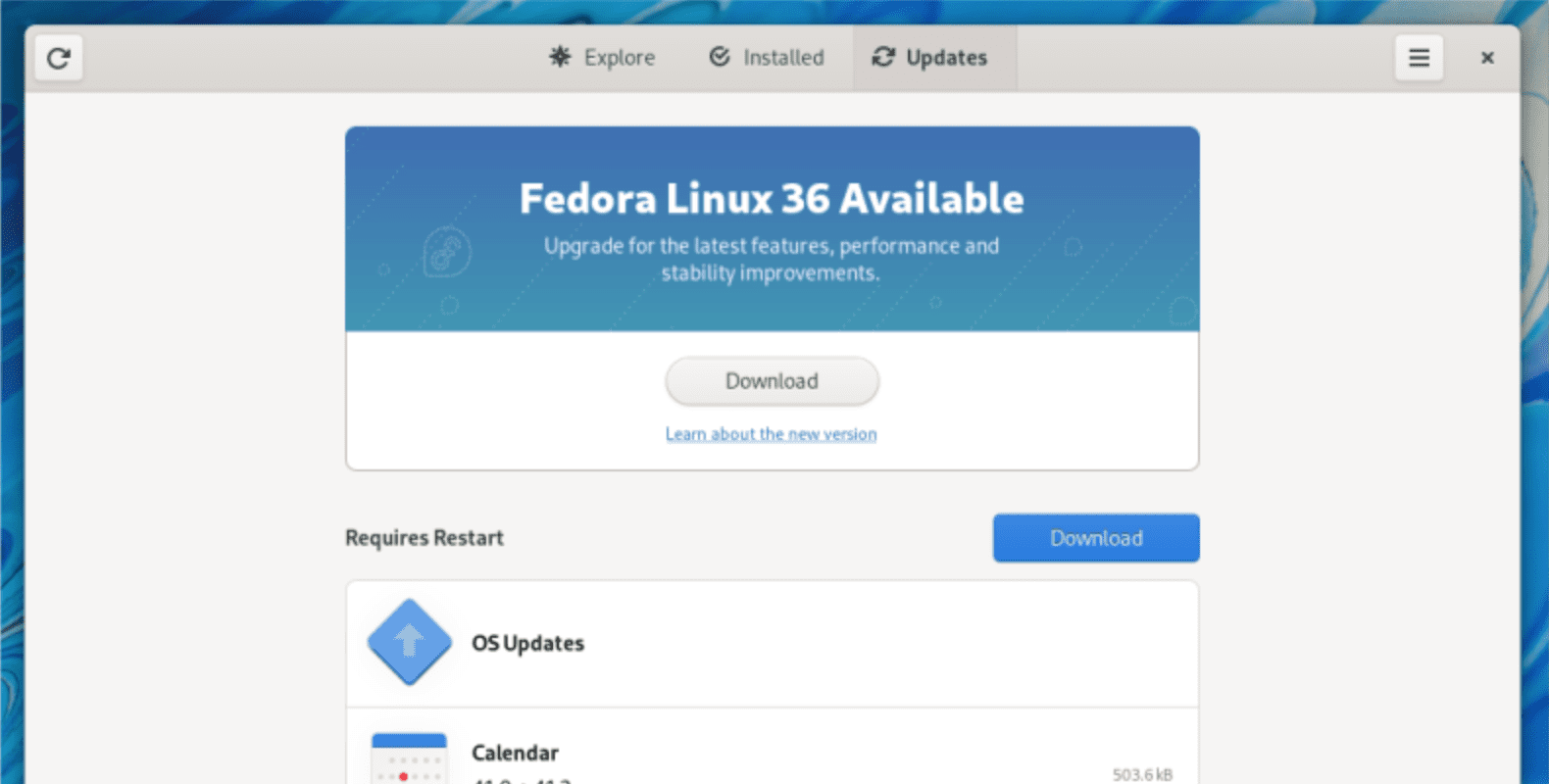
Upgrade to Fedora 36 – GUI
This process might take some time. Upon completion, you will be prompted to restart your system to install Fedora 36.
Conclusion
This post has given you a comprehensive step-by-step guide to upgrading from fedora 35 to Fedora 36 Beta. Do you think we left anything behind? Well, don’t hesitate to let us know in the comments below.

2 comments
Is it ready. I thought Fedora 36 is still in beta
It is in beta. This article suggests enabling some sort of prerelease channel to get Fedora 36 -BETA-, which is a very “do it at your own peril” thing. See this line:
gsettings set org.gnome.software show-upgrade-prerelease true
Karen, I’m sorry, but you’re spreading misinformation. Fedora 36 isn’t out to the masses. When it is, we’ll be able to simply click a button to get it.