GNOME, an acronym for the GNU Network Object Model Environment, is a graphical user interface and set of computer desktop apps for Linux OS users. It is aimed at making Linux OS an easy-to-use OS for non-programmers. With GNOME, you can set the interface to look like Windows or macOS. GNOME is a free and non-proprietary desktop environment for all the major Linux distros, including Fedora Linux, Debian, Ubuntu, Enterprise Linux, Red Hat, SUSE, and others.
On the other hand, a command-line alias cmd, CLI, prompt, console, or terminal refers to a text-based user interface (UI) utilized in viewing, manipulating, handling, running programs, and managing comp files as interacting with the computer. It is much like Windows Explorer or Finder on the macOS but without the graphical interface.
GNOME has emerged as the most efficient, reliable, and stable of all the available desktop environments for Linux while retaining its user-friendliness features. GNOME began as a free and open desktop alternative to proprietary options like KDE at the time, and it has been going strong ever since.
In this article, we will guide you through the required steps to start a GNOME desktop from the command line on Debian, specifically version 11 “Bullseye.” So, let us get underway.
Starting the GNOME desktop environment from the command line
Ensure you have a GNOME desktop environment setup on your machine before starting it up. In case you don’t have the desktop environment installed on your machine, then you can use the following command to set it up on your device:
sudo tasksel install desktop gnome-desktop
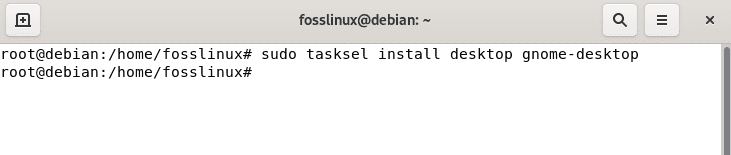
install gnome desktop environment
Now that the environment is set up, to start it, you need to use the Gnome Display Manager(gdm) that aids execute the command. Compared with the general default X window xdm, gdm can directly adjust the settings of the desktop environment from the graphical introduction, and xdm has to edit several xdm settings
To start the Gnome desktop environment or rather close it, you can utilize the following command, and by the way, this is tested in the Gnome 3 environment:
Start command:
sudo /etc/init.d/gdm3 start
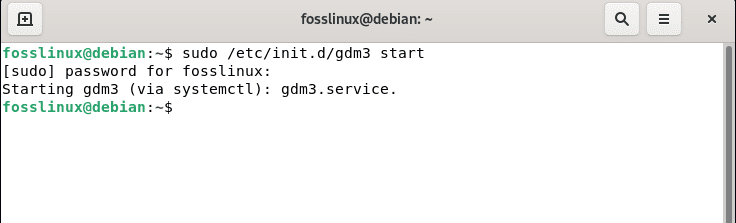
start gnome environment
Stop command:
To put the desktop environment to a stop/halt, run the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/gdm3 stop
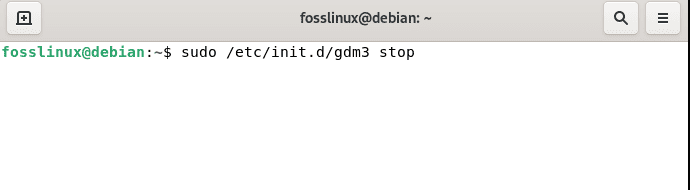
stop gnome environment
Restart command:
To reboot the desktop environment, run the following command:
sudo /etc/init.d/gdm3 restart
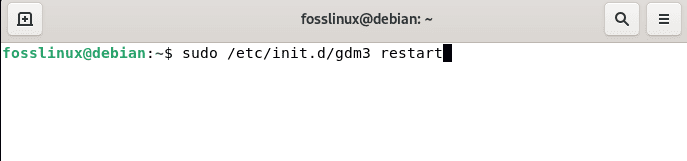
restart gnome environment
Final thoughts
And that’s how you start, stop, and restart the GNOME desktop environment using the command line on Debian. We hope this article came in handy. Keep following FossLinux for more guides.

