RabbitMQ is the most popular free and open source message-queueing or message-broker Software. RabbitMQ originally implemented Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). It also supports protocols such as STOMP (Streaming Text Oriented Messaging Protocol), and MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport).
Generally, message-broker software is used for sending and receiving messages between various kinds of distributed services, systems or applications.
RabbitMQ, which has been written in Erlang programming language, has the following features:
- Support for multiple protocols – AMQP, MQTT, STOMP, HTTP
- Support for client interfaces and libraries for all major programming languages
- Clustering / High Availability
- A diverse set of tools and plugins
- Routing messages between exchanges and queues
- User-friendly web interface to monitor and control message broker
- Tracing capabilities
In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to setup RabbitMQ on Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver).
Installing RabbitMQ on Ubuntu
First, let us update ubuntu repositories:
sudo apt-get update
Add Signing Key using either of the following commands:
wget -O - "https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/2.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc" | sudo apt-key add -
or
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver "hkps.pool.sks-keyservers.net" --recv-keys "0x6B73A36E6026DFCA"
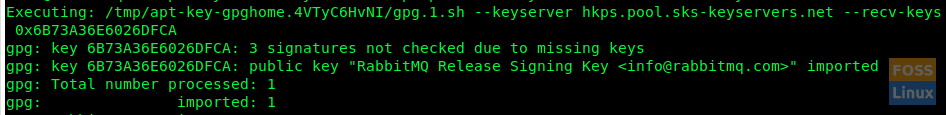
Add Key
Create Rabbitmq repository file.
vim /etc/apt/sources.list.d/bintray.rabbitmq.list
Add following repositories to file.
deb https://dl.bintray.com/rabbitmq-erlang/debian bionic erlang deb https://dl.bintray.com/rabbitmq/debian bionic main
Save and close the file.
Run Repository Update.
sudo apt-get update
Install RabbitMQ Server.
sudo apt-get install rabbitmq-server
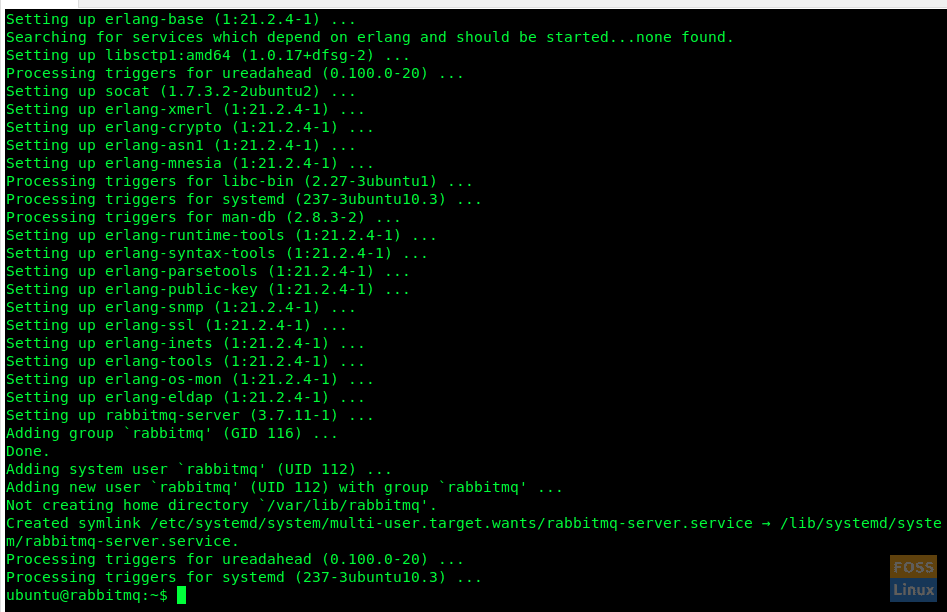
Installation
Check RabbitMQ Server Status.
sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server.service
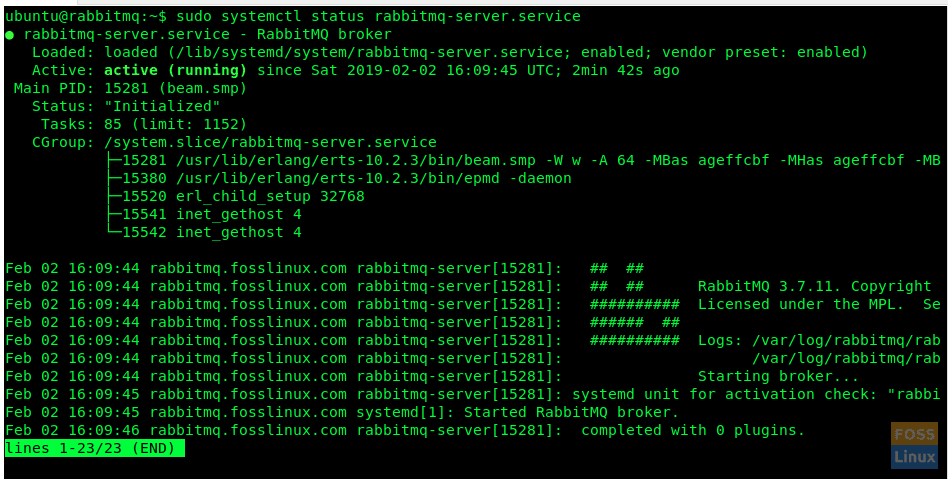
Check Status
If RabbitMQ is not running, then start service with this command:
sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server.service
Enable RabbitMQ service on system boot.
sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
RabbitMQ Ports
4369: epmd, a peer discovery service used by RabbitMQ nodes and CLI tools
5672, 5671: used by AMQP 0-9-1 and 1.0 clients without and with TLS
25672: used for inter-node and CLI tools communication
35672-35682: used by CLI tools (Erlang distribution client ports) for communication with nodes and is allocated from a dynamic range
15672: HTTP API clients, management UI and rabbitmqadmin (only if the management plugin is enabled)
61613, 61614: STOMP clients without and with TLS (only if the STOMP plugin is enabled)
1883, 8883: (MQTT clients without and with TLS, if the MQTT plugin is enabled
15674: STOMP-over-WebSockets clients (only if the Web STOMP plugin is enabled)
15675: MQTT-over-WebSockets clients (only if the Web MQTT plugin is enabled)
Allow RabbitMQ Management UI Through Firewall
RabbitMQ management console runs on port 15672 and it needs to be granted permission via the firewall.
sudo ufw allow 15672
After a successful installation, we can access the web management console and it runs on “15672” port.
But by default, ‘Installation Management Console’ plugin is not enabled. This plugin is needed in order to monitor and manage the RabbitMQ server. It is also used to monitor queues, message rates and manage queues, bindings, and users etc.
Let us see how we can enable the ‘Installation Management Console’ plugin. But before we do that, let us take a look at all the RabbitMQ plugins that are available.
sudo rabbitmq-plugins list
Now enable the RabbitMQ Management plugin
sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
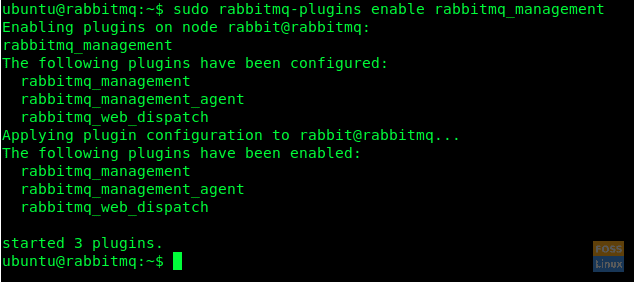
Enable Plugin
We can access the Management console using the default guest user. But we need to create and add a new Admin user to access Management console.
Here we create a user with username ‘admin’ and password is also ‘admin’. But I would recommend using a strong password for security.
sudo rabbitmqctl add_user admin admin
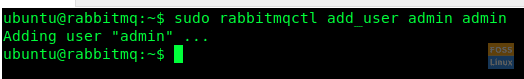
Admin User
Now we tag our user ‘admin’, which we created in the steps above, as ‘administrator’
sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
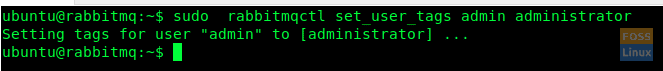
Tag User
Now we are ready to restart RabbitMQ service
sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server.service
Before we access Management UI, let us check the ports on the server
sudo netstat -tunlp
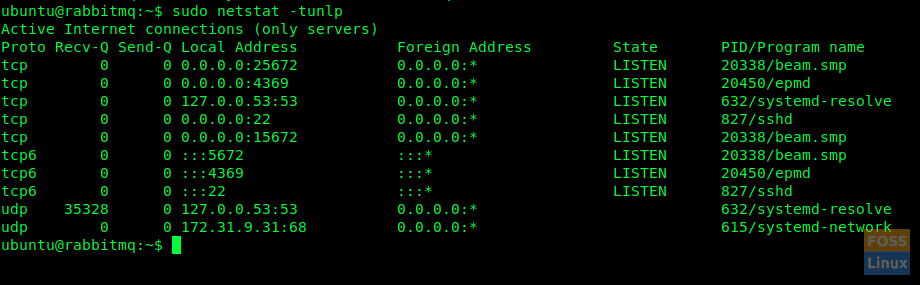
Ports
Management UI access
The Management Console can be accessed using either of these URLs:
- http://ServerIp or
- hostname:15672/
Eg: – http://13.236.85.236:15672 / or http://rabbitmq.fosslinux.com:15672
You will be able to view the console login window.
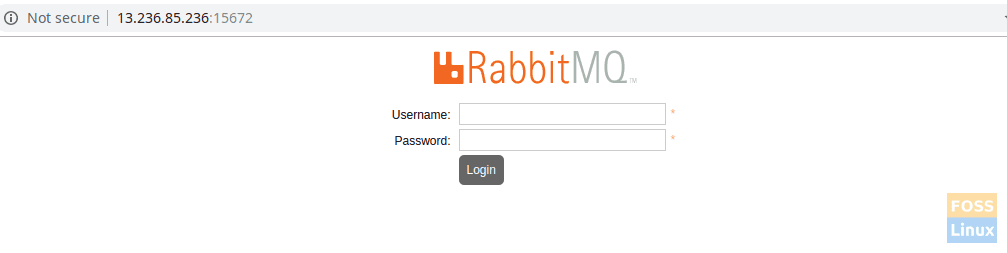
Management Login
Then use the already created admin username and password to access the dashboard.
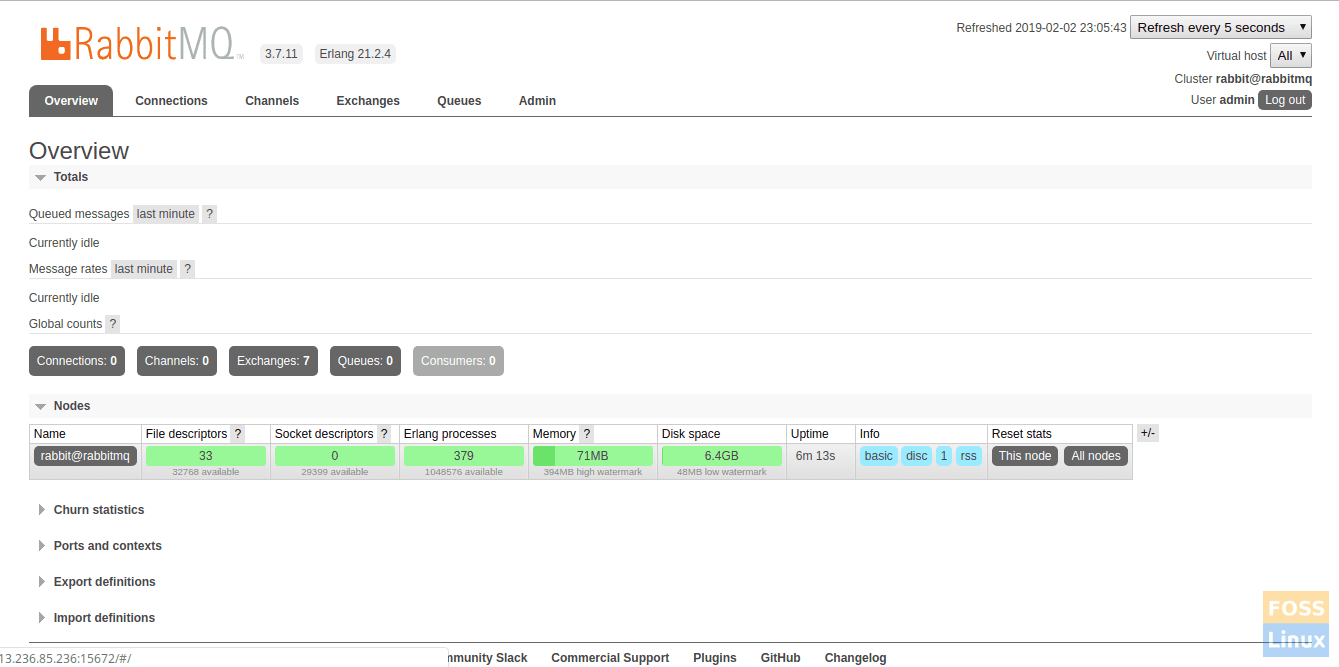
RabbitMQ Management Console
You have successfully installed and configured RabbitMQ server.
If you have any issues or questions feel free to ask in the comments section below.


5 comments
I tried various other websites before this one – this is the only one that worked
Thank you Darshana
I tried various other websites before this one – this is the only one that worked
Thank you Darshana
Great post, straight to the point, and shows the essentials for beginners
Gracias por el tutorial !!!
Thank You Very Much..