File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a popular and widely used tool for transferring files between a server and clients over the network. The major problem with the default FTP settings is the security risk associated with the unencrypted transmission of user credentials and data over the network. This could compromise the user account details.
Hence, there is a need to install a secure server that supports encryption. There are several open-source FTP servers available for Linux at your disposal. The most commonly used servers include Vsftpd, PureFTPd, and ProFTPD.
In this tutorial, we are going to describe how to install and configure VSFTPD server, which is a very secure FTP Daemon.
Installing FTP Server on CentOS
Here we are going to use Centos 7 Minimal installation for demonstration, and root login to execute commands.
Step 1 – Install vsftpd package
Generally, the vsftpd package is available in the default CentOS repositories. Run the following command to install an FTP server.
yum install vsftpd
After the installation check status of FTP service.
systemctl status vsftpd
If service is not started you can start service using below command.
systemctl start vsftpd
now we should enable FTP service on system boot.
systemctl enable vsftpd
Step 2 – Configure the vsftpd
VSFTPD configuration file located at “/etc/vsftpd/” directory . So we are going to modify “vsftpd.conf”. Before modification take backup of the original file.
cp /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.origbackup
Now edit the file.
vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
We are going to allow access to the FTP server only for the local users, So we shall edit the following parameters and modify.
anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES
Find “write_enable” and uncomment the setting to allow changes to the filesystem.
write_enable=YES
Find and uncomment the “chroot” directive to Prevent the FTP users to access any files outside of their home directories.
chroot_local_user=YES
Here we configure FTP directories to allow upload when chroot enabled. This is the recommended method. So add following lines to “vsftpd.conf” file.
user_sub_token=$USER local_root=/home/$USER/ftp
Normally vsftpd can use any port for passive FTP connections. Here we mention a minimum and maximum range of ports for vsftpd.
Add these lines to file
pasv_min_port=40000 pasv_max_port=41000
To limiting user, login add following configurations after the “userlist_enable=YES” line.
userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list userlist_deny=NO
Now save and exit the file.
Restart VSFTPD service.
systemctl restart vsftpd
Step 3 – Configure firewall
Allow FTP ports via firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=20-21/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=40000-41000/tcp
Now reload firewall.
firewall-cmd --reload
Step 4 – Create an FTP user
Add a user. Replace “darsh” with the user name you want.
adduser darsh
Set password for the user.
passwd darsh
Now add the user to the allowed FTP users list. To do that, edit the configuration file and add creed user name.
vi /etc/vsftpd/user_list
Then save and exit the file.
Create an upload directory to the user.
mkdir -p /home/darsh/ftp/upload
Set directory permissions.
chmod 550 /home/darsh/ftp chmod 750 /home/darsh/ftp/upload
Change directory ownership.
chown -R darsh: /home/darsh/ftp
We created a user with shell access and if you want you can disable shell access from the user.
usermod -s /sbin/nologin darsh
Step 5 – Test FTP Server
Now you can use FTP client and access the server. If you don’t have one, I would recommend using the free and open-source app “FileZilla”.
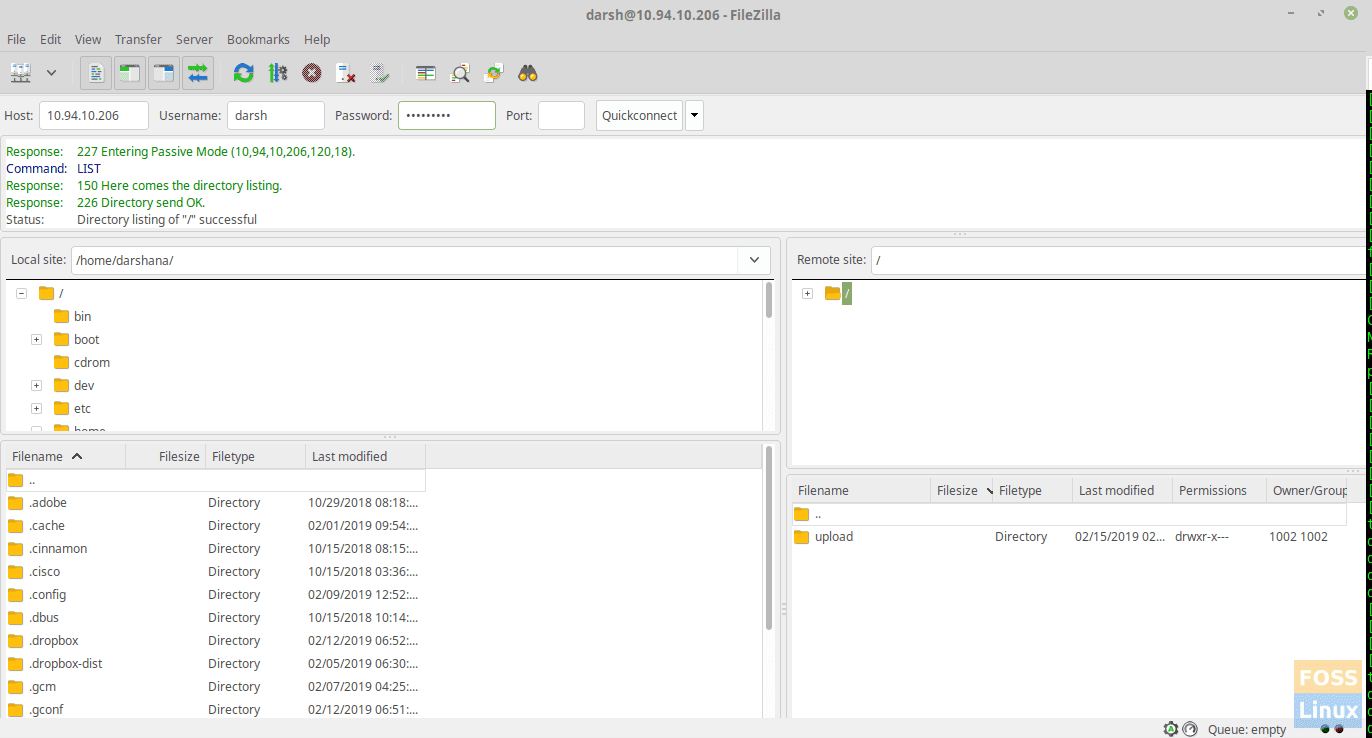
Access FTP Server
You can browse upload directory and create a file for testing.
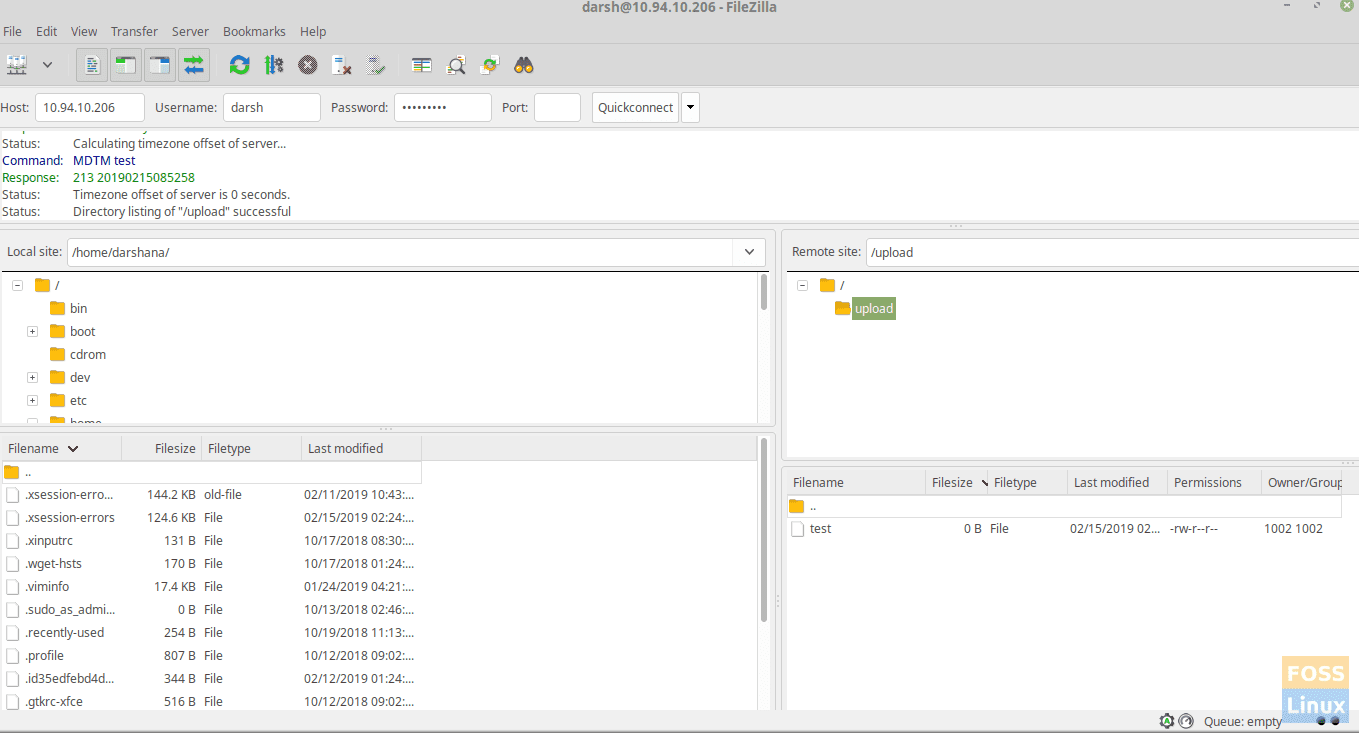
Create Files On FTP Server
That’s it! You have successfully configured an FTP server on CentOS. Let us know how your installation went and do share the article with your friends on social platforms.


1 comment
Thanks for good how to. I was getting access denied message when testing even from the local server using ftp localhost with correct username and password. This is what I had to do on Oracle Linux 8.3 ( which is based on RedHat / CentOS 8.3).
sudo usermod -s /usr/sbin/nologin
sudo nano /etc/shells
/usr/sbin/nologin
and then restart the vsftpd service and I am in. Will be good idea to add this to the article for benefit of others.
Now if I can find out how to install gFTP in Oracle Linux 8.3 (CentOS 8.3 / RedHat 8.3), that will be great. The gftp does not come as standard binary in the repos. Also snapd is not available to install gFTP or filezilla.