Perl is a dynamic interpreted scripting language famous for its powerful text processing abilities. Syntactically it resembles C, but it’s far more compressed, allowing developers to very tourist code like one-liners that hack a solution much faster than other scripting languages.
Most system utilities and application modules for Linux systems are written in Perl. Therefore, it’s not surprising to encounter an error when trying to install a module or execute a script due to a missing Perl module.
Installing missing Perl modules on Debian
Luckily, there are several ways you can use to install missing Perl modules on your system. They include:
- Downloading and installing modules manually
- Installing modules via CPAN
This post will give you a step-by-step guide on ‘How to install missing Perl modules on Debian.’ Let’s get started.
Prerequisite
This post assumes you already have Perl installed on your system. Depending on your Linux distribution, you can use any of the commands below to install Perl.
- Debian
sudo apt install perl
- Arch Linux
sudo pacman install perl
- Rhel, CentOS, Fedora
sudo yum install perl
- OpenSUSE
sudo zypper install perl
[Method 1] Download and Install Perl Modules Manually
This method is pretty straightforward. You download the required module from the official cpan website and install it from the command line. The only technical bit comes in the installation part. Luckily, this post will provide you with all the steps you need to follow.
This post will show you how to install the Gtk2::Ex::Utils Perl module, which is a requirement for most Linux utilities. However, you can use the procedure described here to install any other Perl module your system might need. Follow the steps below.
1. Install “make” on your System
“make” is a Linux command-line utility that enables you to compile and install other system utilities and programs on your system. It is also used to compile and install Perl modules on Linux systems. You will most likely encounter the error “make: command not found” if it’s not installed.
Use any of the commands below, depending on your current distribution, to install “make.”
- Debian
sudo apt install make
- Arch Linux
sudo pacman -S make
- Rhel, CentOS, Fedora
sudo yum install make
- OpenSUSE
sudo zypper install make
2. Download Module from Cpan Website
If you have interacted with the Snap store, a repository where you can download any snap package that you might require, think of CPAN (Comprehensive Perl Archive Network) as an online repository where you can download any Perl library or module. As of writing this post, more than 250,000 Perl modules are available on CPAN.
To download a Perl module, open the official CPAN website and type the module name in the search box. For better results, ensure you type the module’s full name as displayed in the error or the installation file. For example, this post will try installing the Gtk2::Ex::Utils module.

Enter Module Name
After typing the module name, click the “Search” button. You should see a list of Perl modules that include the name you just typed in the search box.
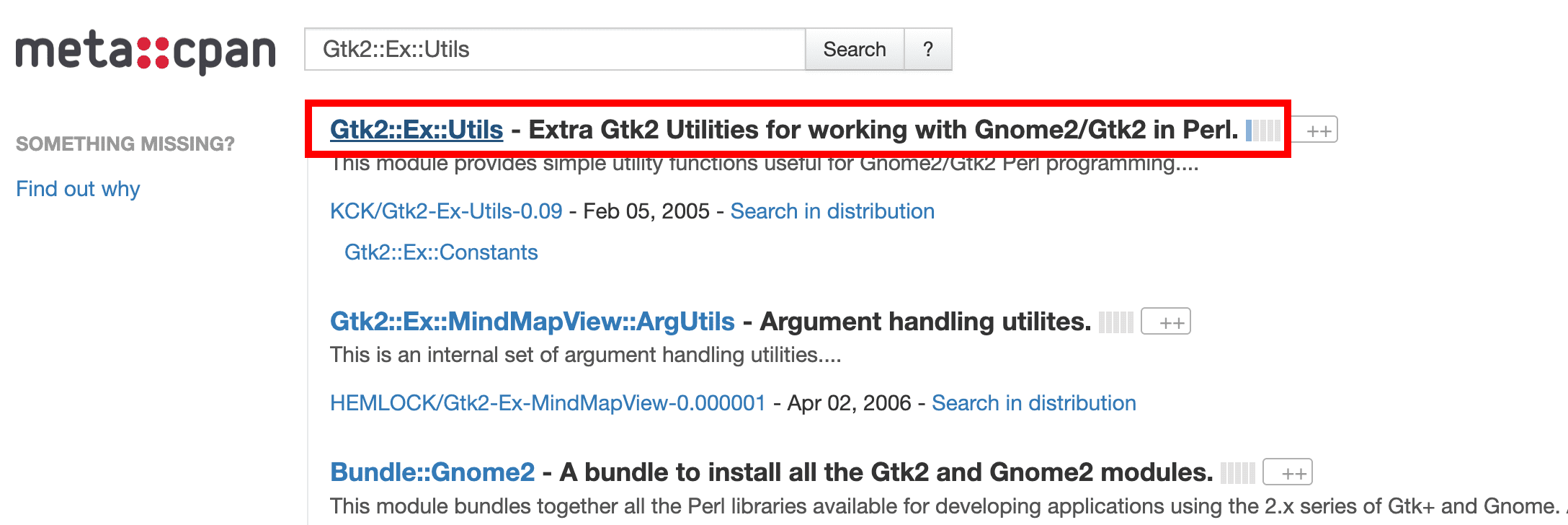
Search Perl Module
Click the module with the exact name you are searching to download. You will see a download option on the left-hand side panel under the Tools menu on the module page. Click it to download the module.
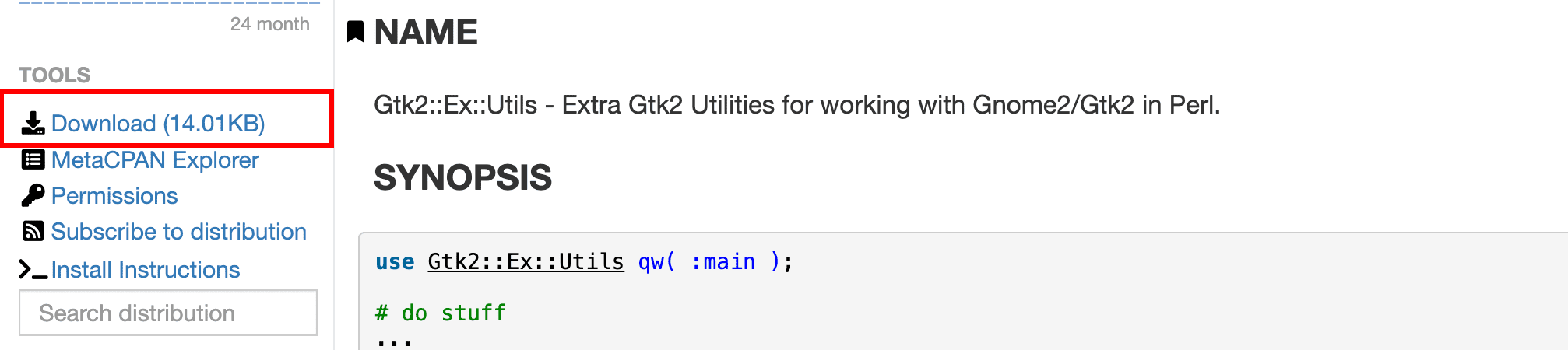
Download Module
3. Extract the File Contents
After successfully downloading the module, you will notice that it’s compressed using the “tar.gz” file format. Launch the Terminal and use the command below to extract it.
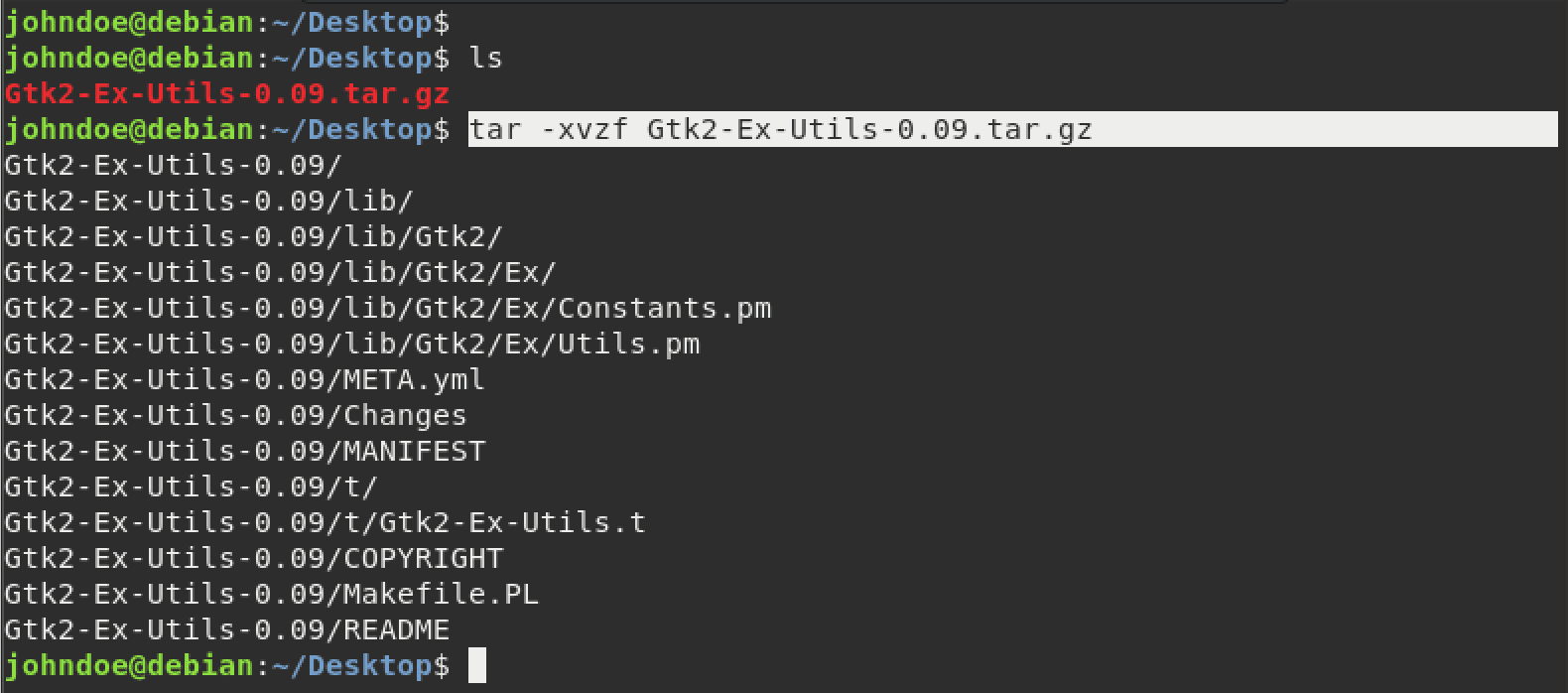
Extract Files
A new folder will ce created which contains the extracted contents. Use the cd command to navigate inside this new folder.
4. Install Module
When you run the ls command, you will see the file “Makefile.PL.” This file is always available in any Perl module. You need to run this file using Perl, as shown below.
sudo perl Makefile.PL
When done, run the make command as shown below.
sudo make
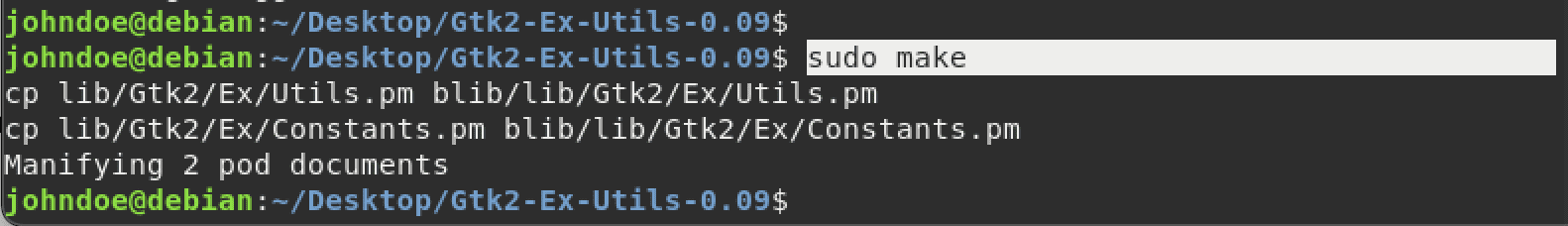
Run make command
Next, you will run the make test command below to check the Perl code for correctness of the functionality.
sudo make test
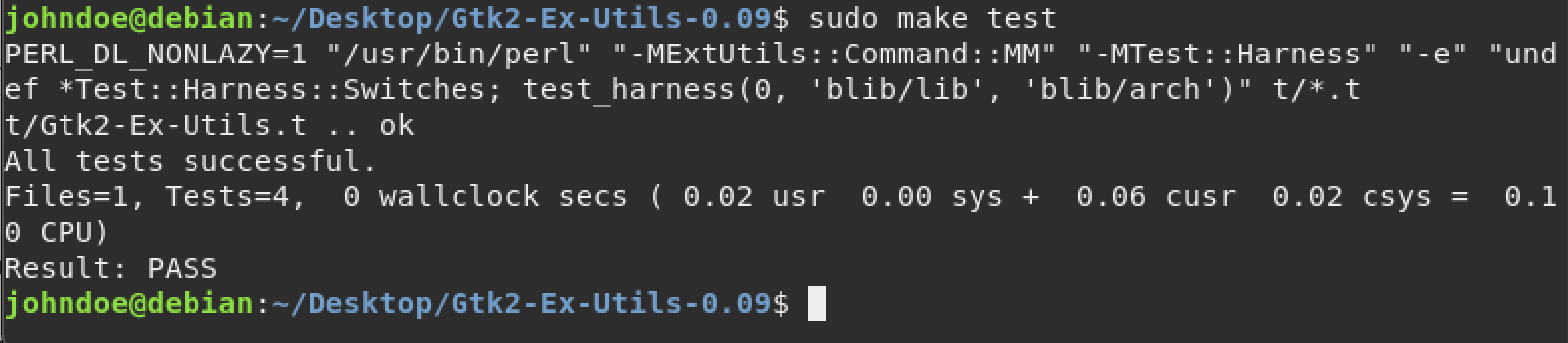
Run make test
From the image, you can see that the module “PASSED” the make test.
Tip: If you get an error/ fail after running the “make test” command, please check the README file and confirm whether the module you are installing depends on another module. For example, the module we installed on this post required we first install the gtk2-perl module.
Next, run the command below.
sudo make install
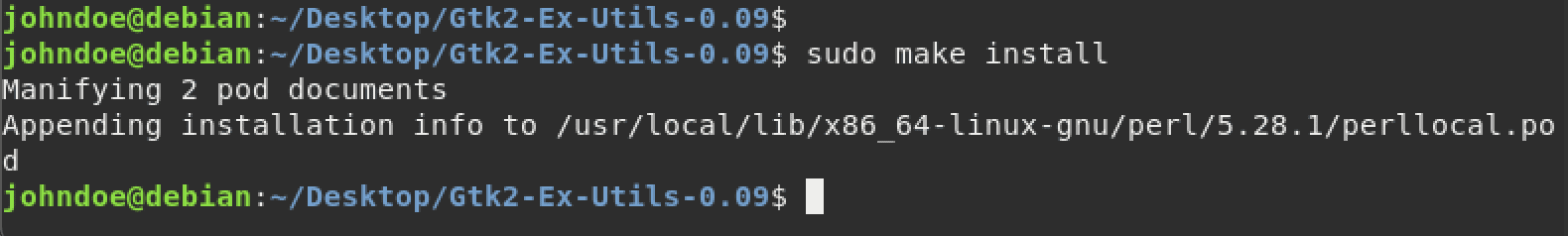
Make install command
That’s it! You have successfully installed the missing Perl modules on your system.
[Method 2] Install Perl modules using cpan
This is one of the easiest methods that you can use to install a missing Perl module on your system. In the previous method, you had to manually download the module from the CPAN website and install it on your Terminal via the command line.
You will download and install the module automatically using the CPAN command-line utility. But, first, launch the CPAN console by executing the command below.
sudo cpan
Next, use the install command to install the module you want, as shown in the image below.
install Gtk2::Ex::Utils
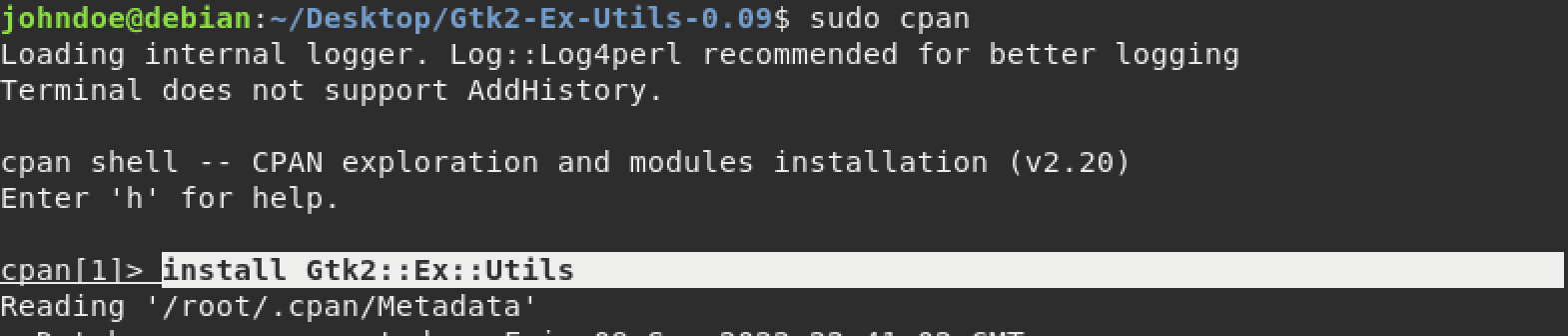
Install Module
This step might take quite some time. Please be patient. If the installation completes without any errors, you have successfully installed the Perl module on your system.
Check Installed Perl Modules
After installing a module or application, verifying whether the module was successfully installed is always recommended. To confirm the installation of Perl modules, you will use a “perldoc.”
Execute the command below to install perldoc on Debian
sudo apt install perl-doc
After a successful install, you can use the command below to check if a module was successfully installed.
sudo perldoc -l [Module-Name]
e.g
sudo perldoc -l Gtk2::Ex::Utils
This command should give you the path of your module.
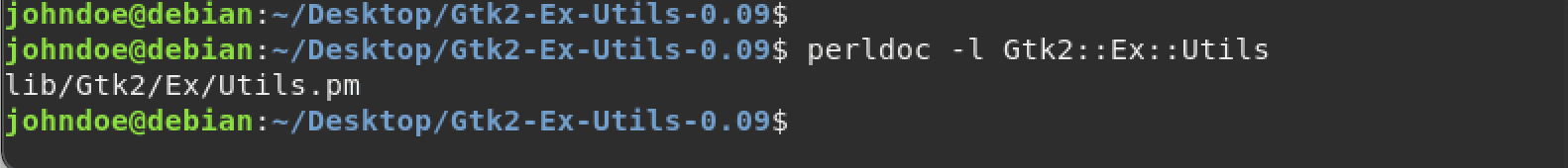
Verify Installation
Conclusion
This post has given you two methods to install missing Perl modules on your system. Let us know which you found most convenient. Did you come across any issues, or do you have any comments regarding this post? Let us know in the comments section below.

