To keep your important files safe, you should create backups of the data regularly. Manual copying of files is tedious and time-consuming. MintBackup is the simple backup solution that comes with Linux Mint.
MintBackup has an elegant user interface and consumes less amount of system resources. It stores the backup in a .tar file. It is easy to configure and serves best if you’re looking for is a simple backup creation program. Let’s burn through its features and how to use it.
MintBackup Tool Features and Usage
1. A simple and straightforward user interface
The program’s instructions and actions are crystal clear even for beginners. It provides the distinction of backing up files or application list, then excluding specific directories and files, and also to include certain hidden files. Anyone can steer through the backup process very quickly and successfully.
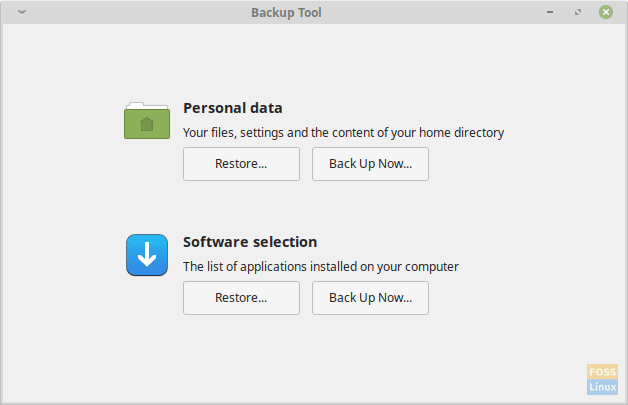
Opening Window
2. File exclusion
MintBackup provides the option to exclude specific files and directories from the backups. By default, the ‘/home/user/Documents/Backups’ directory gets excluded because it’s the directory where the backups get saved. Users can always add directories or files as per their need.
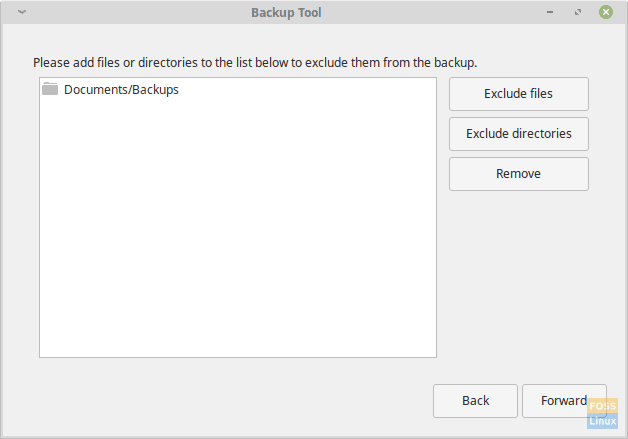
Files exclusion stage.
3. Hidden files inclusion
MintBackup also gives you the option to include hidden directories. In GNU/Linux systems, files and directories are hidden by placing ‘.’ at the front of the name of the directory. You can view the hidden files by using the command:
ls -a
For example, a typical home directory:
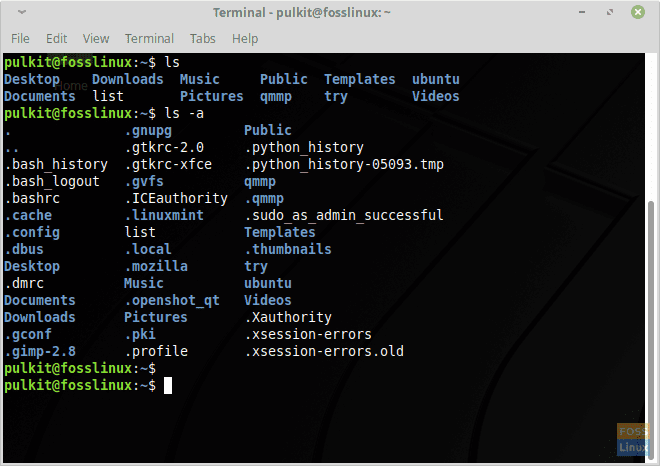
Hidden files in a typical home directory. Notice all those hidden files!
Some of these files contain the configurations of individual programs. Hence, MintBackup provides the options to include the hidden files. We recommend including the .config directory, as it holds all the configuration files of the changes you make to the appearance or preferences of your user account on your system.
4. Application list backup
MintBackup can also perform application list backup, which is not typically available in other backup programs. You can make a backup of the list of applications that you have installed from the application store of your distribution.
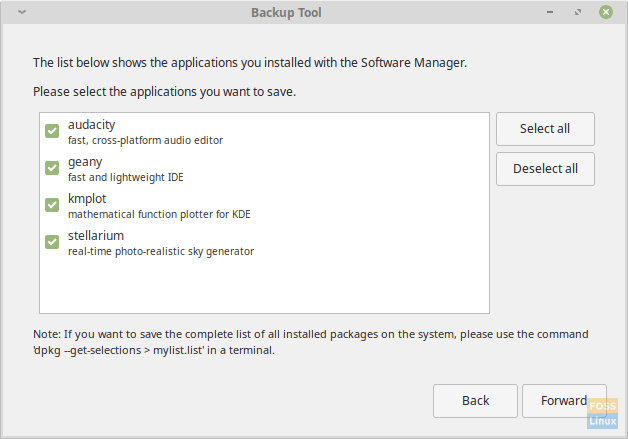
Application list backup menu.
Cons
Application list
A setback of this program is with the application backup settings. It only allows users to create a backup of the list of applications that are installed from the software manager of that distribution. It does give directions for creating the backup of a list of all the applications on the system, but the program should have the option of doing that automatically.
MintBackup recommends using this for a backup of all applications:
dpkg --get-selections > mylist.list
It just stores the name of the applications. We recommend using another command, which displays the list of applications with its description, version, and architecture:
dpkg -l > mylist.list
Both commands should create a file named mylist.list in the home directory, which has the list of all programs on the system.
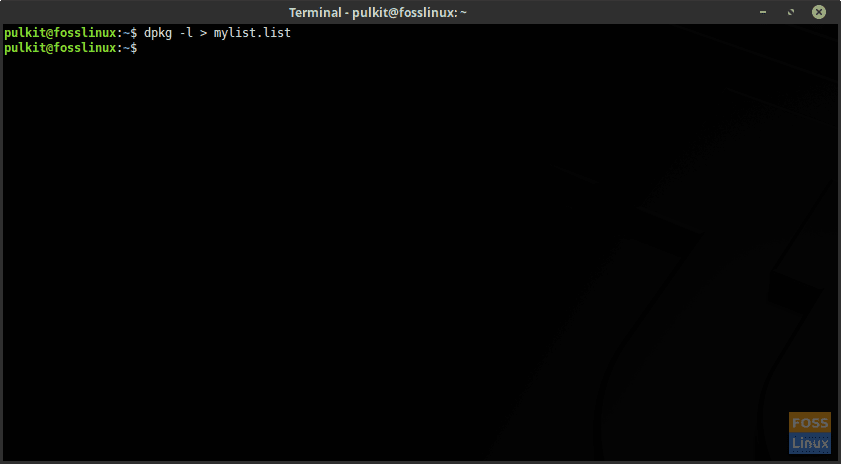
Making a backup of a list of all programs using CLI.
Repetition
MintBackup does provide an option to create the backup on an external drive as well, but every time that a backup gets created, a new backup file is generated by MintBackup. It’s a useful feature because the system might even lose some files between two points of backup, but MintBackup should also provide the option on updating an existing backup file so that lot of time is saved.
The usage of MintBackup is straightforward, open up the program from the main menu ‘Backup Tool’, and follow the on screen.
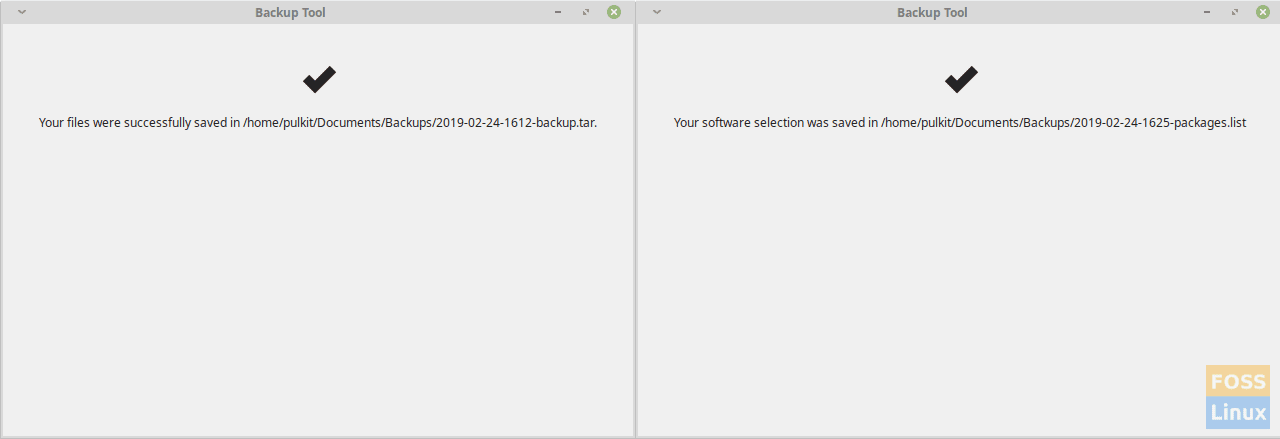
Backup result.
Conclusion
MintBackup is a great backup tool which allows making backups easily without much confusing options or unnecessary ‘features.’ While using Linux Mint, the creation of backups cannot be more comfortable.
Let us know what you think about MintBackup in the comments. Cheers!


5 comments
Guys – I’ve read the article and comments made all the steps, but still no go. I got unresolvable dependency errors on installing g++ and on update I got dependency errors on update finalizer…well after update still unresolvable dependency (as expected because not all updates were not broken). Now I went on and on and installed updates over it and voila – broken packages disappeared and g++ is now installed and working. I wonder if all installations come out so handy as Linux Mint goes 😉 goog luck
One command that you can use for the issue you would be
sudo apt install -f
the -f states to fix broken packages. if the command outputs 0 broken fixed than nothing is broken. I assume you refresh the repository cache before each update or new software installation?
It would be helpful to show how to include hidden files do you need to select all the hidden folders or can you use something like .*
Guys, doing this method encrypted my external hard drive, but I can’t find the password for it. Please help me.
Does not work or download anything or install. It only switches your search engine to Bing!